The participating atoms can be located on the same molecule adjacent nucleotides or on different molecules adjacent nucleotides on different DNA strands. Because there are two hydrogen atoms we call this diatomic hydrogen di meaning two.
 Examples Of Hydrogen Bonding Chemistry Examples
Examples Of Hydrogen Bonding Chemistry Examples
In this example carbon has 4 of 8 electrons in its outer shell and oxygen.

Hydrogen bonding for dummies. Hydrogen bonding interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons. A hydrogen bond results when some of the atoms in a covalently bonded molecule pull the shared electrons to one side of the molecule creating an electrical imbalance in the molecule. In this video we discuss hydrogen bonds.
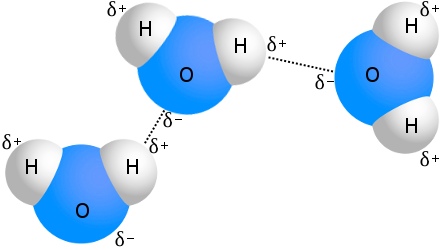
When studying environmental science one type of atomic bond you need to be familiar with is the hydrogen bond. Although stronger than most other intermolecular forces the hydrogen bond is much weaker than both the ionic bondand the covalent bond. Hydrogen bonds can exist between atoms in different molecules or in the same molecule.
Remember that electrons have a negative electric charge. Esters are derived from carboxylic acids and usually alcohol. Hydrogen bonding keeps water in its liquid state over a wider temperature range than for any.
As you would expect the strength of intermolecular hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions is reflected in higher boiling points. Often enhanced by ionic interactions. In chemistry a hydrogen bondis a type of attractive intermolecular forcethat exists between two partialelectric chargesof opposite polarity.
There will also of course be dispersion forces and dipole-dipole attractions between the ester and the water molecules. There are four electron groups around nitrogen three bonding pairs and one lone pair. This is not a sharing of electrons as in a.
One of the slightly positive hydrogen atoms in a water molecule can be sufficiently attracted to one of the lone pairs on one of the oxygen atoms in an ester for a hydrogen bond to be formed. While carboxylic acid has the -COOH group the hydrogen is replaced by a hydrocarbon in an ester. With three bonding pairs and one lone pair the structure is designated as AX 3 E.
Just look at the trend for hexane nonpolar London dispersion interactions only 3-hexanone dipole-dipole interactions and 3-hexanol hydrogen bonding. This is because the oxygen atom in addition to forming bonds with the hydrogen atoms also carries two pairs of unshared electrons. Drug-target hydrogen bond distances are typically within the range of 15-22 Å.
Repulsions are minimized by directing each hydrogen atom and the lone pair to the corners of a tetrahedron. We cover how do hydrogen bonds form the different elements that take part in hydrogen bonds and why doesnt oil a. Hydrogen bonding refers to the formation of Hydrogen bonds which are a special class of attractive intermolecular forces that arise due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another highly electronegative atom which lies in the vicinity of the hydrogen atom.
Drug-target hydrogen bond strengths are typically within the range of 16 to 60 kJ mol-1. Covalent Bonding In covalent bonding electrons are shared between atoms rather than donated in order for the atoms of both elements to gain full outer shells. Such a bond is weaker than an ionic bond or covalent bond but stronger than van der Waals forces.
An example of covalent bonding is the molecule of carbon dioxide. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom and its overall structure is bent. The second atom is usually of a type that strongly attracts electrons such as nitrogen or oxygen.
The American Heritage Student Science Dictionary Second Edition. Electrons are always shared in pairs. Hydrogen bonding reduces extreme temperature shifts near large bodies of water.
Hydrogen bonding allows animals to cool themselves using perspiration because such a large amount of heat is needed to. In other words two hydrogen atoms H are covalently bonded a type of chemical bond together as H-H. Hydrogen bonds are ubiquitous in the body and vary greatly in strength.
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom such as oxygen or nitrogen. A chemical bond in which a hydrogen atom that is already bonded to an atom in a molecule forms a second bond with another atom either in the same molecule or in a different one. All of the electron pairsshared and unsharedrepel each other.
A hydrogen bond is a weak chemical bond that occurs between hydrogen atoms and more electronegative atoms like oxygen nitrogen and fluorine. HR 3 N HR 2 N HRN ROH. The chemical formula of an ester takes the form RCO 2 R where R is the hydrocarbon parts of the carboxylic acid and R is the alcohol.
MOLECULAR HYDROGEN Molecular hydrogen gas or H 2 g is the primary form in which hydrogen is found. This introduction to medicinal chemistry is focussed on the both the strength and distance of these bonds and how they influence these reactions.