Cost-Volume-Profit CVP AnalysisA technique that examines changes in profits in response to changes in sales volumes costs and prices CVP GraphShows the relationship between total revenues and total costs. Cost volume profit chart socialmediaworks via socialmediaworksco How Is Cost Volume Profit Analysis Used for Decision Making via saylordotorggithubio Thanks for visiting our website article 7347 11 Cost Volume Profit Graph Excel Templateuu0312 xls published by Excel Templates Format.
 Cost Volume Profit Analysis And Break Even Point Magnimetrics
Cost Volume Profit Analysis And Break Even Point Magnimetrics
Running this analysis involves using several.

Cost volume profit graph. Look at Exhibit 23 a cost-volume-profit chart for Video Productions a company that produces videotapes. Cost-volume-profit analysis helps you understand different ways to meet your net income goals. Contribution margin indicates how sales affects profitability.
Sales price Sales volume Variable cost Fixed cost The graphs provide a helpful way to visualize. Pipeline monitoring enables you to create a dashboard that makes it simple to determine and also track the phases of a pipe. Meaning of ProfitVolume Graph or Profit Chart.
Below is the CVP graph of the example above. Illustrates how an organizations profits are expected to change under different volumes of activity ch03qxd 92704 406 PM Page 108 SUMMARY 109Uses Describe volume revenues costs and profits. The Cost-Volume-Profit CVP analysis is a method of cost accounting.
The graphical representation of unit sales and dollar sales needed to break even is referred to as the break even chart or Cost Volume Profit CVP CVP Analysis Guide Cost Volume Profit Analysis CVP analysis also commonly referred to as Break Even Analysis is a way for companies to determine how changes graph. Companies can use profit-volume PV charts to establish sales goals. Q Values at breakeven or target profit.
Profit Revenue Fixed Costs Variable Costs. Profit-volume chart is another form of graph used in management accounting to know about business profit level. The variable cost per tape is USD 12 and the fixed costs per month are USD 40000.
Profit 0 50 x 50 00 0. Its usefulness is to show a direct relationship between profit and the volume of sales. First its a simple line graph that almost anyone can understand within seconds.
The break even point is clearly marked and allows a business to see where it will begin to make a profit. In other words its a graph that shows the relationship between the cost of units produced and the volume of units produced using fixed costs total costs and total sales. Use cost volume profit graph excel template to develop.
The profit will be 300000 where the gap between the total revenue and total cost line is 300000 since the gap represents profit after the break-even point or loss before the break-even point A contribution graph shows the difference between the variable cost line and the total cost line that represents fixed costs. It looks at the impact of changes in production costs and sales on operating profits. Profit margin formula in excel is an input formula in the final column the profit margin on sale will be calculated.
How to graph cost revenue and profit functions in excel. A cost volume profit chart often abbreviated CVP chart is a graphical representation of the cost-volume-profit analysis. Break even chart does not directly show the amount of profit.
While contracting this graph different lines for costs and revenues are omitted here since profit points are plotted only. When running a business a decision-maker or managerial accountant needs to consider how four different factors affect net income. It has to be determined by measuring the vertical distance between the sales and total cost lines.
Usage cost volume profit graph excel template to develop. A profit-volume PV chart is a graphic that shows the earnings or losses of a company in relation to its volume of sales. A cost volume profit analysis chart often called a break even chart is a useful tool for businesses for two main reasons.
-Units sold -Revenues -Variable fixed and total. A PV Graph expresses the relationships between profit and volume. Profit volume chart is a straightforward relationship of profits to sales level.
A cost-volume-profit chart is a graph that shows the relationships among sales costs volume and profit. Performing the CVP we calculate the Break-even point for various sales volume and cost structure scenarios to help management with the short-term decision-making process. Where profit is PR revenue equals the product of price per unit P and sales volume in units Q fixed costs FC are constant and total variable costs equal the product of units sold Q and variable cost per unit V the following equation is a more elaborate representation of CVP relationships.
For a simpler graph requiring less typing you don t need to specify dates or other information about the revenue and expenses. The cost-volume-profit analysis makes several assumptions including that the sales price fixed costs and variable cost per unit are constant. Each tape sells for USD 20.
Cost Volume Profit CVP analysis also commonly referred to as Break Even Analysis Break Even Analysis Break Even Analysis in economics financial modeling and cost accounting refers to the point in which total cost and total revenue are equal is a way for companies to determine how changes in costs both variable and fixed Fixed and Variable Costs Cost is something that can be classified.
One way to do this would be to calculate profit at each of the potential profit-maximizing quantities and observe which profit is largest. Determine marginal cost by taking the derivative of total cost with respect to quantity.
 Profit Maximisation Economics Help
Profit Maximisation Economics Help
MRMC is the most important concept in microec.
/Profit-Maximization-1-56a27da93df78cf77276a5ee.png)
Calculating profit maximizing output. If this isnt feasible its also usually possible to tell which quantity is profit maximizing by looking at the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves. The Monopoly maximizes its Profit at the quantity of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Marginal revenue represents the change in total revenue associated with an additional unit of output and marginal cost is the change in total cost for an additional unit of output.
A As a monopolist calculate this firms optimal output Q and price per unit P. In other words it must produce at a level where MC MR. This is the 2nd of 6 videos going through an exam-type question on using quadratic and linear functions to solve business matheconomics problems.
Set up your table. Quantity Total Revenue Total Cost Total Profit Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost. In short three steps can determine a monopoly firms profit-maximizing price and output.
The Monopolist Determines Its Profit-Maximizing Level of Output The firm can use the points on the demand curve D to calculate total revenue and then based on total revenue calculate its marginal revenue curve. Set the equation equal to zero and solve for t. The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price MR MC so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of approximately 85 which is labeled as E in Figure 1 a.
0 200t 50 50 200tSolving for t you get t 14. Determine marginal revenue by taking the derivative of total revenue with respect to quantity. Marginal analysis tells us that the profit-maximizing output is where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
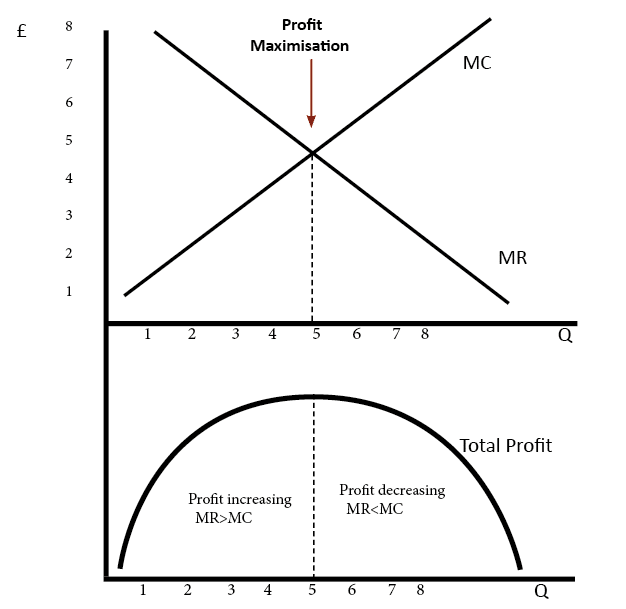
A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue MR marginal cost MC. Using a spreadsheet or piece of paper draw a table with six columns. P - Q.
However maximizing profit does not necessarily mean that economic profit will be earned. In other words it must produce at a level where MC MR. Profit Maximization Rule Definition The Profit Maximization Rule states that i f a firm chooses to maximize its profits it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost MC is equal to Marginal Revenue MR and the Marginal Cost curve is rising.
Calculate and graph the firms marginal revenue marginal cost and demand curves. Profit Maximizing Using Total Revenue and Total Cost Data Instead of using the golden rule of profit maximization discussed above you can also find a firms maximum profit or minimum loss by looking at total revenue and total cost data. Profit Total Revenue TR Total Costs TC.
The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost MC is equal to Marginal Revenue MR and the Marginal Cost curve is rising. Identify the point at which the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect and determine the level of output at. As price per unit declines so demand expands Total revenue rises but at a decreasing rate as shown by the column showing marginal revenue.
Name the columns as follows. Therefore profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. The firms average cost of production is labeled C.
While the function itself represents the total money gained the differentiated. An assumption in classical economics is that firms seek to maximise profits. The Monopolists demand curve.
To maximize profit in perfect competition a firm must set its production output such that marginal revenue the income earned by selling one additional unit of a good is equal to marginal cost the cost of producing one additional unit of a good. A monopolist sets his. In this video I explain how to identify the profit maximizing quantity and calculate total revenue and profit.
Test the surrounding values of t in your. Simply calculate the firms total revenue price times quantity at each quantity. Total profit is maximised at an output level when marginal revenue marginal cost Consider the example in the table.
Profit Total revenueTotal cost PriceQuantity producedAverage costQuantity produced Profit Total revenue Total cost Price Quantity produced Average cost Quantity produced Since a perfectly competitive firm must accept the price for its output as determined by the products market demand and supply it cannot choose the price it charges. Given these equations the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined through the following steps.