One way to do this would be to calculate profit at each of the potential profit-maximizing quantities and observe which profit is largest. Determine marginal cost by taking the derivative of total cost with respect to quantity.
 Profit Maximisation Economics Help
Profit Maximisation Economics Help
MRMC is the most important concept in microec.
/Profit-Maximization-1-56a27da93df78cf77276a5ee.png)
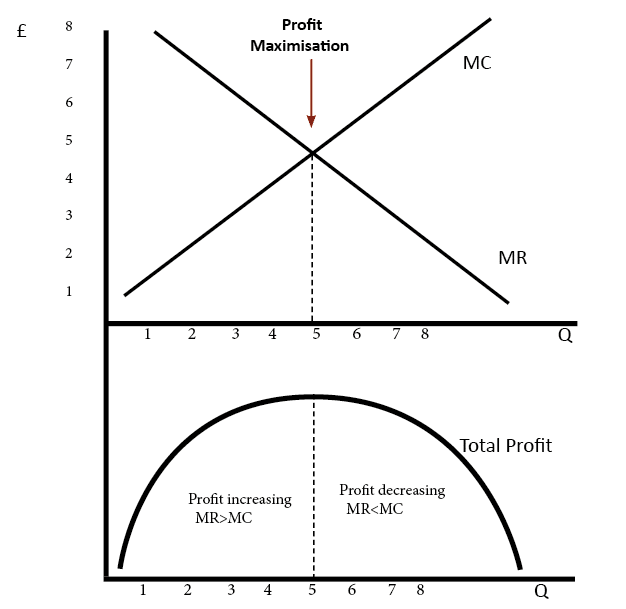
Calculating profit maximizing output. If this isnt feasible its also usually possible to tell which quantity is profit maximizing by looking at the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves. The Monopoly maximizes its Profit at the quantity of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Marginal revenue represents the change in total revenue associated with an additional unit of output and marginal cost is the change in total cost for an additional unit of output.
A As a monopolist calculate this firms optimal output Q and price per unit P. In other words it must produce at a level where MC MR. This is the 2nd of 6 videos going through an exam-type question on using quadratic and linear functions to solve business matheconomics problems.
Set up your table. Quantity Total Revenue Total Cost Total Profit Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost. In short three steps can determine a monopoly firms profit-maximizing price and output.
The Monopolist Determines Its Profit-Maximizing Level of Output The firm can use the points on the demand curve D to calculate total revenue and then based on total revenue calculate its marginal revenue curve. Set the equation equal to zero and solve for t. The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price MR MC so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of approximately 85 which is labeled as E in Figure 1 a.
0 200t 50 50 200tSolving for t you get t 14. Determine marginal revenue by taking the derivative of total revenue with respect to quantity. Marginal analysis tells us that the profit-maximizing output is where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue MR marginal cost MC. Using a spreadsheet or piece of paper draw a table with six columns. P - Q.
However maximizing profit does not necessarily mean that economic profit will be earned. In other words it must produce at a level where MC MR. Profit Maximization Rule Definition The Profit Maximization Rule states that i f a firm chooses to maximize its profits it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost MC is equal to Marginal Revenue MR and the Marginal Cost curve is rising.
Calculate and graph the firms marginal revenue marginal cost and demand curves. Profit Maximizing Using Total Revenue and Total Cost Data Instead of using the golden rule of profit maximization discussed above you can also find a firms maximum profit or minimum loss by looking at total revenue and total cost data. Profit Total Revenue TR Total Costs TC.
The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost MC is equal to Marginal Revenue MR and the Marginal Cost curve is rising. Identify the point at which the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect and determine the level of output at. As price per unit declines so demand expands Total revenue rises but at a decreasing rate as shown by the column showing marginal revenue.
Name the columns as follows. Therefore profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. The firms average cost of production is labeled C.
While the function itself represents the total money gained the differentiated. An assumption in classical economics is that firms seek to maximise profits. The Monopolists demand curve.
To maximize profit in perfect competition a firm must set its production output such that marginal revenue the income earned by selling one additional unit of a good is equal to marginal cost the cost of producing one additional unit of a good. A monopolist sets his. In this video I explain how to identify the profit maximizing quantity and calculate total revenue and profit.
Test the surrounding values of t in your. Simply calculate the firms total revenue price times quantity at each quantity. Total profit is maximised at an output level when marginal revenue marginal cost Consider the example in the table.
Profit Total revenueTotal cost PriceQuantity producedAverage costQuantity produced Profit Total revenue Total cost Price Quantity produced Average cost Quantity produced Since a perfectly competitive firm must accept the price for its output as determined by the products market demand and supply it cannot choose the price it charges. Given these equations the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined through the following steps.