In response to a signal from another neuron sodium- Na and potassium- K gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential. 8 and propagates along the muscle fibre to its ends.
 Nerve Impulse Conduction Online Biology Notes
Nerve Impulse Conduction Online Biology Notes
The area turns into a stimulus for the adjacent region of the membrane that turns depolarised.
Mechanism of nerve impulse. The previous membrane is repolarised as a result of the exit of the sodium ions from the cell. Nerve impulse is an overall physiological changes that occur in a neuron due mechanical chemical or electrical disturbance created by a stimulus. Thus the propagation of the nerve impulse can be carried out automatically in living systems.
In this paper we elucidate and research in detain and deeply the mechanism of form of the nerve impulse and its features of propagation. Origin of Nerve impulse. And nerve cells where the nerve impulse is set up usually at the region between the cell body of the cell soma and the nerve fibre axon at a site.
Through a chain of chemical events the dendrites part of a neuron pick up an impulse thats shuttled through the axon and transmitted to the next neuron. This is just the mechanism of propagation of the nerve impulse along the nerve l fiber cell membrane. This depolarization results in an action potential which causes the nerve impulse to move along the length of the axon.
Transmission of Nerve Impulse Polarization. Nerve impulses have a domino effect. All the nerve fibres carry information in the form of nerve impulse.
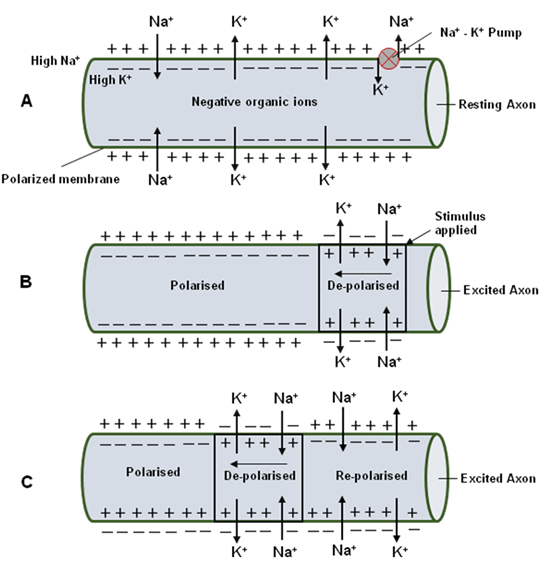
Nerve impulse is the sum total of physical and chemical disturbances created by a stimulus electrical chemical or mechanical in a neuron or nerve fibre which result in the movement of a wave along the nerve fibre. In resting nerve cells the surface is positively charged and the interior is negatively charged. The sodium-potassium pump maintains an electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a neuron when it is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse.
The nerve fibre or axon is like a cylinder the interior of which is filled with axoplasm ie the cytoplasm of the nerve cell and the exterior of which is covered with a thin membrane the axon membrane or. Nerve Impulse transmission along Neuron. Researchers at Linköping University Sweden have discovered a new mechanism by which substances can open a certain type of ion channel and thereby regulate nerve impulses.
Mechanism of Transmission of Nerve Impulse. Originstimulation of nerve impulse B. Process of transmission of Nerve Impulse Resting Membrane Potential.
Propagation travelling of nerve impulse. From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia As an action potential nerve impulse travels down an axon there is a change in polarity across the membrane of the axon. It is the graded potential state where the threshold stimulus having a potential of -55 mV brings a.
Among those that do are striated muscle fibres where the action potential is set up at the point of innervation by the motor nerve as a consequence of neuromuscular transmission see Chap. The axon or nerve fibres are in the form of a cylinder wherein the interior of the axon is filled with axoplasm and the exterior is covered with axolemma. It propagation through axon synapse and neuromuscular junction is called Nerve Impulse conduction.
Nerve impulse transmission through Synapse When nerve impulse reaches the pre-synaptic knob it depolarized the presynaptic membrane and causes the opening of voltage gated calcium channel. Conduction of Nerve Impulse - This video defines nerve impulse and explains the mechanism involved in the transmission of nerve impulse. When a nerve impulse is generated there is a change in the permeability of the cell membrane.
Diffusion of Ca ion in the presynaptic knob causes movement of synaptic vesicle to the surface of the knob. The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron. The cell is now depolarised.
It is a state of resting potential which is electrically charged but non-conductive. A nerve impulse is an electrical phenomenon that occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. An action potential occurs when the nerve cell is in an excited state while conducting nerve impulses.
The solution is in the ionic form that is present in axoplasm and extracellular fluid or ECF. The sodium ions flow inside and potassium ions flow outside causing a reversal of charges. Each neuron receives an impulse and must pass it on to the next neuron and make sure the correct impulse continues on its path.
It is the. The membrane of an unstimulated neuron is polarizedthat is there is a difference in electrical charge between the outside and inside of the membrane. The resting membrane potential refers to the non-excited state of the nerve cell at rest.
This difference at the site through the plasma membrane is referred to as a nerve impulse or action potential. When the surface is stimulated the stimulated point becomes negative. Hence the conduction of impulses.
The inside is negative with respect to the outside. The study published in. The propagation of nerve impulse involves two major parts A.
The nerve fibres are immersed in ECF.