Metal blue nonmetal yellow or metalloid red. Three metals iron cobalt and nickel are magnetic.
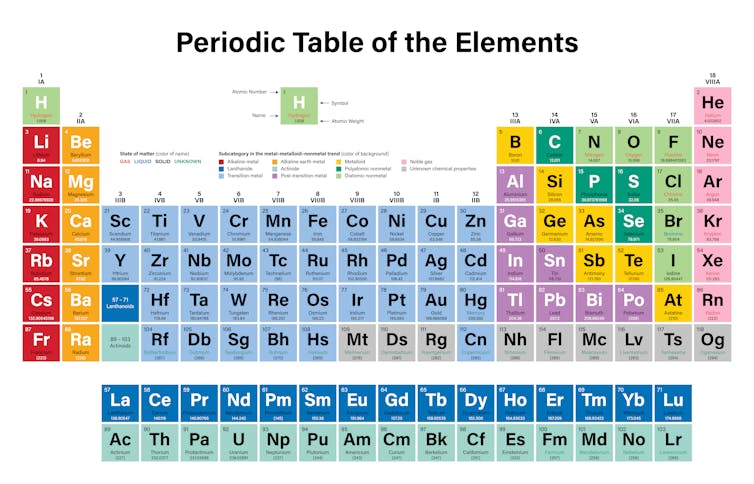 Understanding The Periodic Table Through The Lens Of The Volatile Group I Metals
Understanding The Periodic Table Through The Lens Of The Volatile Group I Metals
The metals are subdivided into separate groups such as basic metals transition metals alkali metals alkaline earth metals rare earth lanthanides and actinides.

Metal in periodic table. The archetypal transition metals and the physically and chemically weak post-transition metals. The metals consist of the alkali metals alkaline earths transition metals lanthanides and actinides. Metal elements are on the left of a stepped line starting at B-Al-Si non-metal elements are on the right of the stepped line.
Examples of metals are gold aluminium copper iron lead silver platinum uranium and zinc. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell.
This periodic table groups elements according to type. Nearly 75 of all the elements in the Periodic Table are classified as metals. Most elements are metals.
Metals In The Periodic Table So because most elements of the Table are metals it makes sense to begin by looking at them. Heavy metals up to the vicinity of iron in the periodic table are largely made via stellar nucleosynthesis. If you look at the Periodic table you will find that the metal elements are located between atomic number 5 Boron B all the way to atomic number 84 Polonium Po.
Although separate on the periodic table lanthanides and actinides are really specific types of transition metals. The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of. At room temperature all of the metals are solids except for mercury which is a liquid.
The metal elements are on the left of a stepped line. From left to right in the periodic table these categories include the highly reactive alkali metals. Many scientists describe a transition metal as any element in the d-block of the periodic table which includes groups 3 to 12 on the periodic table.
In the Periodic Table metals are separated into the groups detailed in the following list. There may be many unforeseen applications that arise from learning about the. They are grouped together in the middle to the left-hand side of the periodic table.
The highlighted elements are considered the metal elements. The IUPAC definition defines a transition metal as an element whose atom has a partially filled d sub-shell or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell. One ounce of gold can be easily converted to 40 meters long wire.
In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. The less reactive alkaline earth metals lanthanides and radioactive actinides. In this process lighter elements from hydrogen to silicon undergo successive fusion reactions inside stars releasing light and heat and forming heavier elements with higher atomic numbers.
In the periodic table. Hence Gold is the most malleable metal in the. The majority of elements on the periodic table are metals.
This group includes alkali metals alkaline earth metals transition metals basic metals lanthanides rare earth elements and actinides. All of the metals are grouped. The periodic table also known as the periodic table of elements is a tabular display of the chemical elements which are arranged by atomic number electron configuration and recurring chemical propertiesThe structure of the table shows periodic trendsThe seven rows of the table called periods generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right.
Most elements can be considered metals. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. Metals and non-metals There are many divisions in the Periodic Table but one of the most important is between the metals and the non-metals.
Gold and silver are the most malleable metal present in the periodic table. 75 of all the elements on the periodic table are metals. Steel is a mixture of elements but it is mostly iron so it is also magnetic.
Such chemistry also explains why mercury metal is a liquid at room temperature despite periodic table predictions. The other metal elements are not magnetic.
Add to my workbooks 5 Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Add to Microsoft Teams. The key consideration is to explain the context for the taxonomy in use.
 Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals Element Classification Groups
Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals Element Classification Groups
The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.

Metalloids in periodic table. Boron B Silicon Si Germanium Ge Arsenic As Antimony Sb Tellurium Te Polonium Po. Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. 70 metals or metalloids are found between nonmetals on the periodic table of the elements.
The list of metalloids in the periodic table are as follows. Metalloids 7 Some books say the term Metalloid is out-dated. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals.
The Periodic Table contains a lot of useful information on the elements. Metalloids The metalloids are a group of elements in the periodic table. Metalloids are instead shown as occurring in a diagonal band or diffuse region.
7261 amu Number of ProtonsElectrons. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. Other authors have suggested classifying some elements as metalloids emphasizes that properties change gradually rather than abruptly as one moves across or down the periodic table.
One of the best ways to classify the elements is into metals and non-metals. 9th to 12th Age. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND.
Metalloids are present on the non-metal side of the periodic table. The metalloids or semimetals are located along the line between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table. Using it you should be able to classify all the elements in different ways.
There is no single property which can be used to unambiguously identify an element as a metalloid. They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
Metals Nonmetals Metalloids periodic table ID. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals. The exact elements considered to be metalloids are somewhat up for debate with different classification systems considering different elements metalloids.
The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids. Some periodic tables distinguish elements that are metalloids and display no formal dividing line between metals and nonmetals. Metals nonmetals and metalloids make up the periodic table with metals constituting the large majority of all metals.
32 Number of Neutrons. They are located to the right of the post-transition metals and to the left of the non-metals. Metalloids-Metalloids are the group of certain elements which has both the properties of the metal and the non-metal.
A big hunk of Silicon is the very definition of metal-yet-not-metal. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image.
In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. The Wooden Periodic Table Table by Theodore Gray. Periodic Table Other contents.
Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. Because these elements have intermediate properties its sort of a judgment call as to whether a particular element is a metalloid or should be assigned to one of the other groups. The term is normally applied to a group of between six and nine elements boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and possibly bismuth polonium astatine found near the center of the P-block or main block of the periodic table.
These elements are called metalloids. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals.
Elements in this range have properties intermediate between nonmetals and metals. 41 Date of Discovery. Metalloids have some properties in common with metals and some in common with non-metals.
Nonsense its a very fine name and it accurately describes these weird in-between elements.
You can identify them easily on the Periodic table because they are presented in the shape of a step ladder. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals.

Periodic Table Name_ Block _ Date_ 7.

Metalloid on periodic table. Some of the metalloids such as silicon and germanium are useful in semi-conductors. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals.
In this lesson youll learn the definition of a metalloid as well as the. The metalloid elements are found in the middle of the periodic table at the point where the metals and nonmetals meet. Recognition status as metalloids of some elements in the p-block of the periodic table.
Percentages are median appearance frequencies in the lists of metalloids. Metalloids are present on the non-metal side of the periodic table. Metalloids The metalloids are a group of elements in the periodic table.
Franz Muller von Reichenstein. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po. Elements in this range have properties intermediate between nonmetals and metals.
Some of the elements of the Periodic table are classified as semimetals or metalloids. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. The elements which are found in the step-like line between metals and nonmetals of the periodic table are known as the metalloids.
What is the definition of the term metalloid. Metalloids-Metalloids are the group of certain elements which has both the properties of the metal and the non-metal. They are located to the right of the post-transition metals and to the left of the non-metals.
Antimony Sb germanium Ge silicon Si arsenic As tellurium Te polonium Po boron B and astatine At. The list of metalloids in the periodic table are as follows. CHEMISTRY- Extra Credit Topic 2.
Because they share properties that are considered to be a cross between non-metals and metals. The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids. They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals.
Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. The exact elements considered to be metalloids are somewhat up for debate with different classification systems considering different elements metalloids. Coloring of glass and ceramics thermoelectric devices.
The staircase-shaped line is a typical example of the arbitrary metalnonmetal dividing line found on some periodic tables. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table. These elements are called metalloids.
Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals. View Ex Cr Metal Nonmetal Metalloidpdf from CHEM 101 at Ehove Career Center. Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals.
In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. The term is normally applied to a group of between six and nine elements boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and possibly bismuth polonium astatine found near the center of the P-block or main block of the periodic table. Metalloids In The Periodic Table.
70 metals or metalloids are found between nonmetals on the periodic table of the elements. All about metalloid metalloid is only exit p- blockNote- in ncert B is not exist in metalloid. Metalloids have some properties in common with metals and some in common with non-metals.
Boron B Silicon Si Germanium Ge Arsenic As Antimony Sb Tellurium Te Polonium Po. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image. Metalloid in chemistry an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having properties intermediate between those of a typical metal and a typical nonmetal.
What type of element is Iron. Looking at the Periodic Table how can you determine if an element is a metal metalloid or nonmetal.
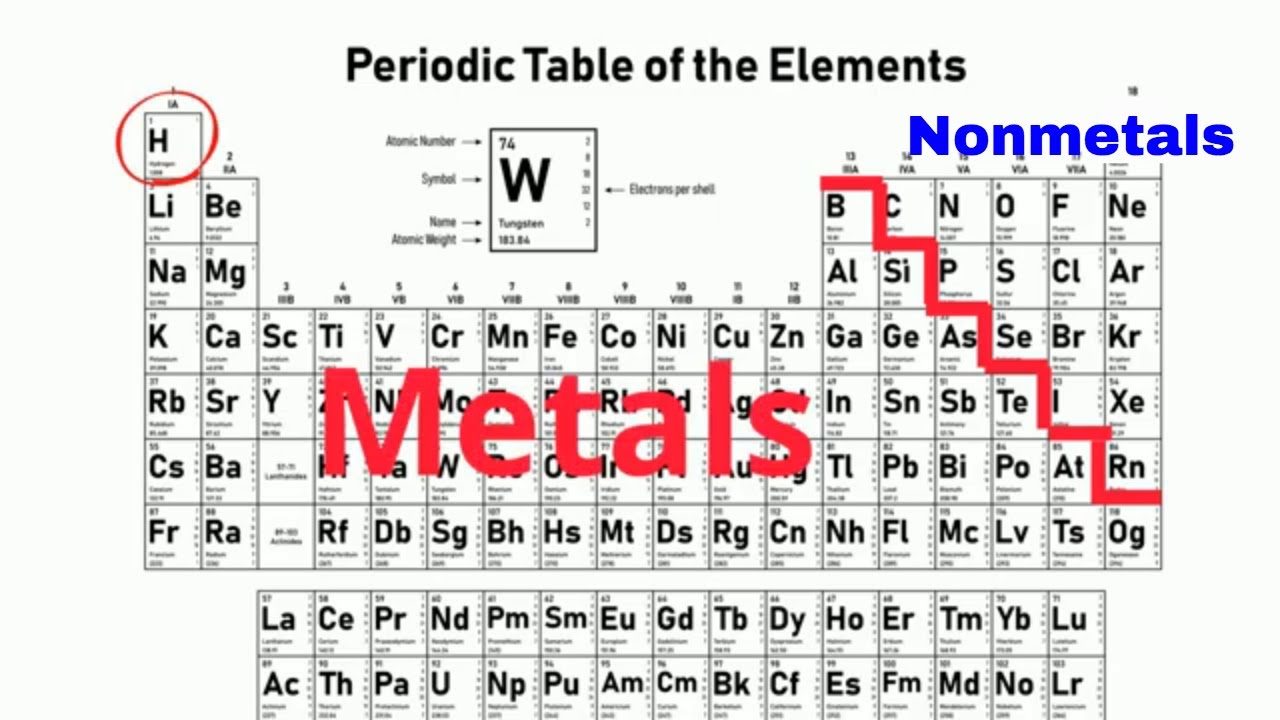 How To Identify Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids On The Periodic Table Youtube
How To Identify Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids On The Periodic Table Youtube
The only exception to this is atomic number 1 Hydrogen H which has a different location on the table.

Metal metalloid nonmetal periodic table. A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the left-hand side of the period. The metals are found on the left and the nonmetals are found on the right. Properties of Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids are discussed and you see where to find them on the periodic table.
The elements can be placed in the periodic table. CHEMISTRY- Extra Credit Topic 2. One useful way is by metals nonmetals and metalloids.
View Ex Cr Metal Nonmetal Metalloidpdf from CHEM 101 at Ehove Career Center. The metal elements are on the left of a stepped line. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
Play this game to review Periodic Table. Metalloids are present on the non-metal side of the periodic table. Non-metals can be easily located on the Periodic Table because they are to the right of the line that looks like a stepping ladder.
The position of an element provides information about its properties. Iron is a good conductor malleable and magnetic. Non-metals are characterized by having the exact opposite properties of metals.
2 Show answers Another question on Chemistry. The periodic table is organized in families and periods. These elements are called metalloids.
Start studying Periodic Table Metal Metalloid or Nonmetal. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
So non-metals are brittle instead of solid. On many periodic tables a jagged black line see figure below along the right side of the table separates the metals from the nonmetals. When will le chateliers principle come into effect.
Report an issue. The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine. From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases.
Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Metals and non-metals There are many divisions in the Periodic Table but one of the most important is between the metals and the non-metals. Nonmetals Metals Metalloids.
And they are not ductile you cannot make them into thin wires or malleable they can not be made into thin sheets. The metals are to the left of the line except for hydrogen which is a nonmetal the nonmetals are to the right of the line and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals.
Most elements are metals with different properties to those of non-metals. Learn about the metals nonmetals and metalloids and the periodic table. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Using the periodic table you can classify the elements in many ways.
Examples of metalloids are Silicon germanium etc. Periodic Table Name_ Block _ Date_ 7. The noble gases are almost completely inert.
Metals are grouped on the left side of the periodic table with an exception. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals.
Metalloids Metals Nonmetals.
Metals are elements having the highest degree of metallic behavior. For example using a.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Periodic-Table-Metals-56a12db33df78cf772682c44.png) What Are The Parts Of The Periodic Table
What Are The Parts Of The Periodic Table
You can imagine a zig-zag.
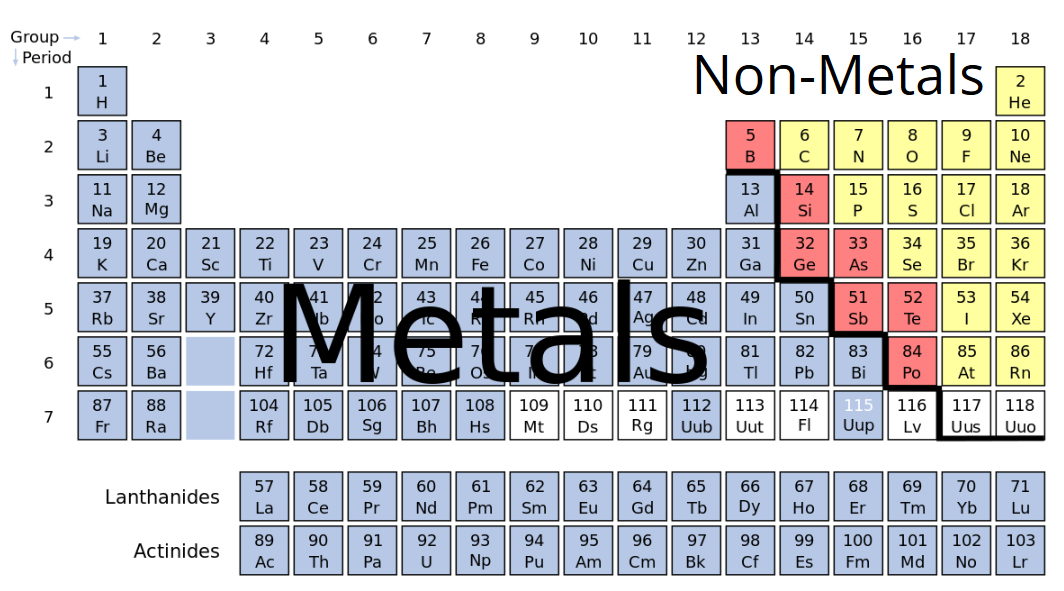
Periodic table metals vs nonmetals. Preview this quiz on Quizizz. The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine. Block in the.
This includes the alkali metals alkaline earth metals transition metals lanthanides and actinides. 9th - 12th grade. The noble gases are almost completely inert.
32 Using The Periodic Table Worksheet. What Do Metalloids Metals and Nonmetals Have In Common. These elements are shown in the following figure.
From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases. Metals have a certain luster or shine while non-metals are dull. Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table whereas non-metals are found on the right side of the periodic table.
Nonmetals have properties opposite those of the metals. Some nonmetals are liquids. Getting To Know Periodic Table Worksheet.
Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. _____ _____ _____ Why are the non-metals grouped together. Metals are flexible and ductile while nonmetals are not.
Color smell physical state. Be sure to use different colours to distinguish the two and provide a key at the bottom of the table. It is a non-metal since it belongs to group 17 of the periodic table.
Notice that metals and non-metals have opposite properties to each other. Which of these is a property of metals. Metals nonmetals and metalloids make up the periodic table with metals constituting the large majority of all metals.
Are found on the left hand side of the periodic table and the non-metal elements are found on the right. Nonmetals however come in different colors. Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table.
Posts Related to Periodic Table Metals And Nonmetals Worksheet. Why are the metals grouped together. Metals react with oxygen to form basic oxides whereas non-metals react with oxygen to form acid oxides.
What physical properties are used to classify elements as metals non-metals or metalloids. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. The Periodic Table contains a lot of useful information on the elements.
Metals vs Non-Metals vs Metalloids FAQs. Metals oxides rust non-metals periodic table reactions. The nonmetal elements occupy the upper right-hand corner of the periodic table.
The nonmetals are brittle not malleable or ductile poor conductors of both heat and electricity and tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions. Why are the. Metalloids tend to exhibit some properties of metals and non-metals.
Elements just to the left of the line may be termed metalloids or semimetals and have properties intermediate between those of the metals and nonmetals. Identify the following as metals nonmetals or metalloids using the periodic table. These elements have similar chemical properties that differ from the elements considered metals.
The periodic table of metals and nonmetals can be broken down to give you a sense of each elements characteristics. Metals vs Non-Metals samabrhms11 2019-05-30T1439350100. Silicon b fluorine c uranium d mercury e arsenic f iridium.
Metals form positively charged ions. Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Definition. Metals usually come in solid forms while nonmetals can be solid liquid or gas.
Is BR a Metal or Non-Metal. Metals have a low ionization enthalpy while non-metals have a high ionization enthalpy. Understand how to use electrical conductivity and the acid-base character of oxides to classify elements as Metals or Non-metals.
Periodic Table And Periodic Law Worksheet. These elements and those to the right of them are nonmetals. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
On the periodic table metals are separated from nonmetals by a zig-zag line stepping through carbon phosphorus selenium iodine and radon. The nonmetals in the periodic table. Play this game to review Periodic Table.
Metals vs Nonmetals DRAFT. Nonmetals include the nonmetal group the halogens and the noble gases. Elements to the far right of the periodic table are nonmetals.
Position in the Periodic Table. Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. Home Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 Chemistry Revision Notes The Periodic Table Metals vs Non-Metals.
The nonmetal element group is a subset of these elements. Metals and non-metals in the periodic table. It is usually easy to tell metals and non-metals apart but some tests are more reliable than others.
Which of these is a property of metals. Metals Vs Nonmetals Dot Diagrams Ions Answers. But non-metals form negatively charged ions metals form basic oxides some of which dissolve to form alkaline solutions but non-metals form acidic oxides.
List three differences in the physical properties between metals and nonmetals. Metals Vs Nonmetals Dot Diagrams Ions. Metalloids can conduct electricity but not as well as metals.
Metals generally form basic oxides while nonmetals are good oxidizing agents. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups.