Energy frac12 times moment. Rotational Kinetic Energy 2 Rotational Kinetic Energy Energy associated with rotation is given by an equation analogous to that for straight-line motion.
Rotational Kinetic Energy And Angular Momentum
Rotational Kinetic Energy RK e 2-1 Moment of Inertia Angular velocity 2.
Rotational kinetic energy formula. The Earth has a moment of inertia I 80410 37 kgm 2. W τ θ W τ θ. Rotational kinetic energy has important effects.
The angular velocity ω 2 rads. Rotational kinetic energy and angular momentum. For an object that is rotating only.
K E 12 I ω 2. K R frac12 I ω 2. Lets carry on madly working out equations applying to rotational motion by substituting the appropriate rotational variables into the straight-line motion equations.
Flywheels for example can be used to store large amounts of rotational kinetic energy in a vehicle as seen in Figure 3. The rotational kinetic energy of the mill stone can be found using the formula. ½ Σmr 2 ω 2.
The rotational kinetic energy of the DVD can be found using the formula. What is the rotational kinetic energy of the object. The kinetic energy of the rotating DVD is 2888 J.
Rotational Kinetic Energy Formula. Rotational kinetic energy K R frac12 Moment of inertia Angular velocity 2 Dimensional formula of moment of inertia M 1 L 2 T 0. If you put a lot of work into rotating an object the object starts spinning.
The rotational kinetic energy K E Solution. The formula of the rotational kinetic energy. Therefore it has a rotational kinetic energy of 213810 29 J.
The mechanical work applied during rotation is the torque times the rotation angle. The Formula for Rotational Energy. We know that rotational kinetic energy is given as.
E 05 I ω² Where E is the rotational kinetic energy in Joules. 11-1-99 Sections 87 - 89 Rotational work and energy. Where M Mass.
Dimensional Formula of Rotational Kinetic Energy. K rot ½ m 1 ω 2 r12 ½ m 2 ω 2 r22. 1 Now Σmr 2 is known as moment of inertia I which is the rotational equivalent of mass or inertia.
An example is the calculation of the rotational kinetic energy of the Earth. K E the rotational kinetic energy kg m 2 s 2 I the moment of inertia. The instantaneous power of an angularly accelerating body.
K 2888 J. And when an object is spinning all its pieces are moving which tells a physicist that it has kinetic energy. If a rigid body is rotating about a fixed axis with angular velocity ω omega ω and a force is applied on it to increase its angular speed and thus rotational kinetic energy then the relation between the work done by the torque of the force and the change in its kinetic energy is predicted by work-kinetic theorem for rotation.
The rotational kinetic energy of the mill stone is 48 000 J. The angular acceleration is equal to the final angular velocity divided by the time and the average angular velocity is equal to half the final angular velocity. 2 What is the rotational kinetic energy of a DVD digital video disc with a moment of inertia of I 100010-4 kgm 2 rotating at an angular velocity of 7600 radianss.
Inertia times angular. The expression for rotational kinetic energy is exactly analogous to translational kinetic energy with I being analogous to m and ω to v. For spinning objects you have to convert from the linear concept of kinetic energy to the rotational concept of kinetic.
To calculate the kinetic energy of rolling motion let us first consider the linear kinetic energy of a body with mass m which is moving with a velocity of v. The moment of inertia I 1 kg m 2. Rotational Kinetic Energy Definition Formula Units Rotational Motion Rotational energy occurs due to the objects rotation and is a part of its total kinetic energy.
The Formula for Rotational Kinetic Energy We can compute it with the following Rotational Kinetic Energy Formula. The dimensional formula of Rotational Kinetic Energy is given by M 1 L 2 T-2. For an object that is moving but not rotating.
The objects rotational kinetic energy is the sum of the kinetic energies of all the particles. Linear kinetic energy ½ m v 2. For an object that is rolling ie translating and rotating simultaneously the total kinetic energy of.
Erotational 1 2I ω2 E rotational 1 2 I ω 2 where ω ω is the angular velocity and I I is the moment of inertia around the axis of rotation. It follows that the rotational kinetic energy given to the flywheel is equal to the work done by the torque. If the rotational energy is considered separately across an objects axis of rotation the moment of inertia is observed.
Dimensional formula of angular velocity M 0 L 0 T-1. Rotational Kinetic Energy Dimensional Formula. The particles that are further from the rotation axis possess more rotational kinetic energy than the ones closer to the rotational axis.
As the Earth has a period of about 2393 hours it has an angular velocity of 72910 5 rads. 1 Since the moment of inertia MOI Mass Radius of Gyration 2. The position of the point mass from the axis of rotation also determines its energy.
K 48 000 J. Rotational Kinetic Energy Formula The following equation is used by the calculator to determine the rotational kinetic energy of an object. Rotational kinetic energy can be expressed as.
Total energy of spring system is always conserved. How much change of kinetic energy occurs while the object moves from the.
 Kinetic Energy Equation For Spring Tessshebaylo
Kinetic Energy Equation For Spring Tessshebaylo
Our elastic potential energy calculator uses the following formula.
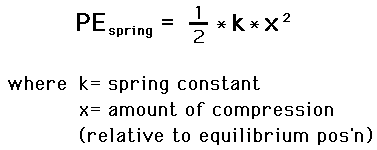
Kinetic energy of spring. The total energy of the ideal mass-spring system is constant. Learn about kinetic and gravitational potential energy. A quarter of the way through a cycle all that potential energy has gone to kinetic as the mass passes through.
But otherwise yes you must integrate through the length of the spring since each part of the spring moves at a different speed moving faster the further away from the fixed end. Total energy12kx2 potential energy at some compression or extension of y is. That energy is called elastic potential energy and is equal to the force F times the distance s.
K is the spring constant. U ½kΔx 2. In this Physics video on work energy and power in Hindi for class 11 we discussed on the conservation of energy in spring block system and explained how pote.
In a simple harmonic oscillator the energy oscillates between kinetic energy of the mass K frac12mv 2 and potential energy U frac12kx 2 stored in the spring. However the total energy of the system will remain constant according to the law of the conservation of energy. Spring contains the kinetic energy only when it is released from position of some compression or extension in it.
The potential energy of the ideal mass-spring system is equal to the work done stretching or compressing the spring. A 2xT 2 B T 2 2k C 2kT 2 D T 2 2x. Then it starts slowing down as it heads over to negative.
The amount of kinetic energy possessed by a moving object depends on the mass of the object and its speed. B Force or tension T kx Hookes Law. In physics you can examine how much potential and kinetic energy is stored in a spring when you compress or stretch it.
Eventually at half a cycle the spring is maximally compressed and the energy is all potential again. In the SHM of the mass and spring system there are no dissipative forces so the total energy is the sum of the potential energy and kinetic energy. KE 12 mv2 and PE 12 ks2.
This is because energy is slowly radiated by the. Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its movement. Consider a spring of mass M equilibrium length L0 and spring constant k.
At the same time the spring is maximally compressed or stretched and thus stores all the mechanical energy of the system as potential energy. The kinetic energy of the spring is equal to its elastic potential energy ie. But gravity will also do work on the ball Demo of Spring Launcher Work of Spring on ball ½ kx2 ½ mv2.
Endgroup Steeven Apr 12 17 at 1422. So just like the case of a vibrating pendulum a vibrating mass on a spring has the greatest potential energy when it has the smallest kinetic energy. Hence x Tk.
12mv2 12kx2 when the spring is stretched some distance x from the equilibrium point and when its mass also has some velocity v with which it is moving. A car travelling along a straight road has kinetic energy of 180 kJ. At these two positions - A and E - the velocity is 0 ms and the kinetic energy is 0 J.
Spring potential energy equation. It is a proportionality constant that describes the relationship between the strain deformation in the spring and the force that causes it. If a spring extends by x on loading then the energy stored by the spring is Given T is the spring force and K is force constant.
A 054 kg object suspended from an ideal spring of spring constant eq27 fracNm eq is oscillating vertically. The kinetic energy of the ideal mass-spring system is given by the motion of mass. And it also has the smallest potential energy position C when it has the greatest kinetic energy.
The brakes are applied and it is brought to rest over a distance of 60 m. A Consider a spring as described above that has one end fixed and the other end moving with. The work done to stretch or compress the spring by a distance L is 05kx2 where x L L0.
This is negligible compared to the work by the spring and so the launch speed is So and the initial kinetic energy is 0 so using the work-energy theorem. At the extremes of its displacement the mass is at rest and has no kinetic energy. Energy stored in the spring k x 2 2 T 2 2k.
In many cases you would assume the spring mass negligible to avoid this issue so that all kinetic energy is given to the object. Of course for a real mass moving with a real spring the motion will eventually come to a stop. Total energy Kinetic energy potential energy This applies to a mass oscillating on a spring so we can easily calculate the total energy using the equations for kinetic energy of a mass and the potential energy stored in a spring.
We usually ignore the kinetic energy of the moving coils of a spring but lets try to get a reasonable approximation to this. The kinetic energy of the mass is zero since the mass is temporarily stopped. The work you do compressing or stretching the spring must go into the energy stored in the spring.
So while the mass moves up and down energy changes forms between potential energy due to the spring potential energy due to gravity and kinetic energy.
In other words it changes depending on an objects height or distance and the mass of the object. The brakes are applied and it is brought to rest over a distance of 60 m.
 Physics For Kids Potential Energy
Physics For Kids Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy at the top kinetic energy at the.
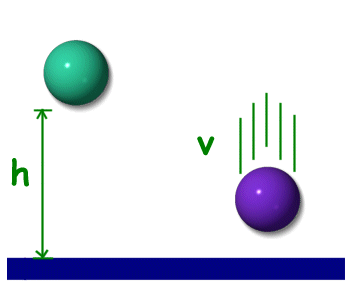
Gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy. As the bag did not get to Mr. PE due to gravity m g h. M is the mass in kilograms kg.
The gravitational potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy as the ball rolls down the ramp. At the highest point B Kinetic energy is zero and Gravitational potential energy is highest. Kinetic energy and work done.
A moving object has kinetic energy because work has been done on it. As garyp said the missing kinetic energy is that of rotation. Due to the Principle of Conservation of Energy we can say that.
PHYS - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy. When an object falls its gravitational potential energy is changed to kinetic energy. A moving car has a lot of kinetic energy.
With escape velocity in a direction pointing away from the ground of a massive body the object will move away from the body slowing. Kinetic energy KE is energy of motion. When the PE is due to an objects height then.
The gravitational potential energy decreases and the. Struggling to get your head round revision or exams. E_p is the gravitational potential energy in joules J.
More generally escape velocity is the speed at which the sum of an objects kinetic energy and its gravitational potential energy is equal to zero. The relationship between potential energy and kinetic energy is that potential energy can transform into kinetic energy. After they jump this potential energy gets converted into kinetic energy and heat as they speed up.
Energy Transfer Gravitational Potential Energy to Kinetic Energy. It will also define aphelion and perihelion. Converting Between Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy.
G is the gravitational field strength. An object which has achieved escape velocity is neither on the surface nor in a closed orbit of any radius. Learn about kinetic and gravitational potential energy.
Or E_p mgh. The gravitational potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases. Here is some additional information that should help you.
These skydivers have potential energy due to being high up. Assuming the yo yo rolls down its string without slipping the translational kinetic energy of the center of mass CM plus the rotational energy of the rotating yo yo about its CM equals the difference in potential energy based on initial height minus final height of. You can use this relationship to calculate the speed of the objects descent.
This lesson will explain how potential energy kinetic energy speed and gravity are linked to the orbital motion of planets in our solar system. Gravitational potential energy for a mass m at height h near the surface of the Earth is mgh more than the potential energy would be at height 0. The gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
Our tips from experts and exam survivors will help you through. Learn about kinetic and gravitational potential energy. From PE to KE.
A car travelling along a straight road has kinetic energy of 180 kJ. The difference in gravitational potential energy of an object in the Earth-object system between two rungs of a ladder will be the same for the first two rungs as for the last two rungs. Red it starts falling from point B downwards due to gravity.
When an object with Gravitational Potential Energy starts to fall its G PE is transferred into Kinetic Energy. Is stored in stretched or squashed materials. Learn about kinetic and gravitational potential energy.
The gravitational potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy as the ball rolls down the ramp. Elastic potential energy will be stored in this catapult when its bands are stretched Gravitational potential energy. As the bag moves upwards kinetic energy decreases and gravitational energy increases.
Gravitational potential energy mgh. Potential energy is position relative. Gravitational potential energy may be converted to other forms of energy such as kinetic energy.