Add to my workbooks 5 Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Add to Microsoft Teams. The key consideration is to explain the context for the taxonomy in use.
 Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals Element Classification Groups
Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals Element Classification Groups
The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.

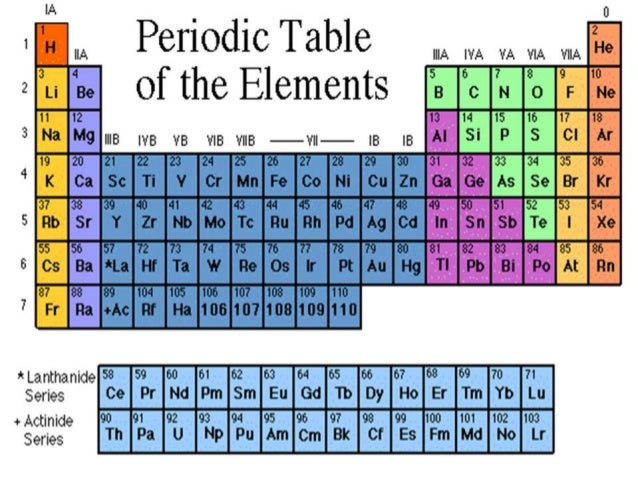
Metalloids in periodic table. Boron B Silicon Si Germanium Ge Arsenic As Antimony Sb Tellurium Te Polonium Po. Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. 70 metals or metalloids are found between nonmetals on the periodic table of the elements.
The list of metalloids in the periodic table are as follows. Metalloids 7 Some books say the term Metalloid is out-dated. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals.
The Periodic Table contains a lot of useful information on the elements. Metalloids The metalloids are a group of elements in the periodic table. Metalloids are instead shown as occurring in a diagonal band or diffuse region.
7261 amu Number of ProtonsElectrons. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. Other authors have suggested classifying some elements as metalloids emphasizes that properties change gradually rather than abruptly as one moves across or down the periodic table.
One of the best ways to classify the elements is into metals and non-metals. 9th to 12th Age. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND.
Metalloids are present on the non-metal side of the periodic table. The metalloids or semimetals are located along the line between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table. Using it you should be able to classify all the elements in different ways.
There is no single property which can be used to unambiguously identify an element as a metalloid. They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
Metals Nonmetals Metalloids periodic table ID. Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals. The exact elements considered to be metalloids are somewhat up for debate with different classification systems considering different elements metalloids.
The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids. Some periodic tables distinguish elements that are metalloids and display no formal dividing line between metals and nonmetals. Metals nonmetals and metalloids make up the periodic table with metals constituting the large majority of all metals.
32 Number of Neutrons. They are located to the right of the post-transition metals and to the left of the non-metals. Metalloids-Metalloids are the group of certain elements which has both the properties of the metal and the non-metal.
A big hunk of Silicon is the very definition of metal-yet-not-metal. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image.
In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. The Wooden Periodic Table Table by Theodore Gray. Periodic Table Other contents.
Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. Because these elements have intermediate properties its sort of a judgment call as to whether a particular element is a metalloid or should be assigned to one of the other groups. The term is normally applied to a group of between six and nine elements boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and possibly bismuth polonium astatine found near the center of the P-block or main block of the periodic table.
These elements are called metalloids. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals.
Elements in this range have properties intermediate between nonmetals and metals. 41 Date of Discovery. Metalloids have some properties in common with metals and some in common with non-metals.
Nonsense its a very fine name and it accurately describes these weird in-between elements.
For example sulfur and carbon are both non-metals. An Introduction to General Organic and Biological Chemistry 12th Identify each of the following elements as a metal a nonmetal or a metalloid.
 Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids
Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids
Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals.
Metals and nonmetals metalloids. Take up the quiz below and find out. Typical nonmetals have a dull coloured or colourless appearance. Are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Introduction to Metals Non Metals and Metalloids. Trends based on Groups Formal Charges 99 Practice Problems. SOLIDS LIQUIDS or GASSES.
Somewhere between metals and nonmetals lie metalloids or semiconductors Let us identify the. What factors should we consider while distinguishing these three. Metalloids tend to be economically important because of their unique conductivity properties they only partially conduct electricity which make them valuable in the semiconductor and computer chip industry.
Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. VINotebook Metals Non-metals MetalloidsMpptx - Metals Nonmetals and Presented by Kesler Science Metalloids Vers 072020 u00a9 Kesler Science LLC Reflect. Metals nonmetals and metalloids are elements that are found in the earth.
These elements are called metalloids. Most or some elements in each category share a range of other properties. A few elements have properties that are either anomalous given their category or otherwise extraordinary.
What is the difference between them. Metalloids are metallic-looking brittle solids that are either semiconductors or exist in semiconducting forms and have amphoteric or weakly acidic oxides. And have acidic oxides.
Where is between metals and metalliods. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND. In chemistry we learn about metals non-metals and metalloids.
Are brittle when solid. They react with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide. The metalloids or semimetals have properties that are somewhat of a cross between metals and nonmetals.
The main difference between metals nonmetals and metalloids is that metals show the highest degree of metallic behavior and nonmetals do not show metallic behavior whereas metalloids show some degree of metallic behavior. The main difference between metals non-metals and metalloids are that metals are elements that are hard malleable fusible shiny ductile and good conductors. Discussion of the properties of each.
Non-metals do not have properties present in metals whereas metalloids are elements that have intermediate properties of both metals and non-metals. The exception is hydrogen H the first element on the periodic table. Metals can be found on the left side of the periodic table while nonmetals are found on the right side.
Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids. Where at the metalloids located on the Periodic Table. Metals form oxides that are basic but non-metals form oxides that are acidic.
Most of these elements are used in various applications. Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. Can a metalloid have properties of metals and nonmetals.
Mercury a metal has a low melting point and exists as a liquid at room temperature graphite a form of carbon a non-metal has a high boiling point and is also a good conductor of electricity A. Elements to the far right of the periodic table are nonmetals. Questions and Answers 1.
Metals are _____ and can be drawn into a wire.
Properties of Metalloids They conduct electricity and heat better than nonmetals but not as well as metals. From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases.
 Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids On The Periodic Table Youtube
Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids On The Periodic Table Youtube
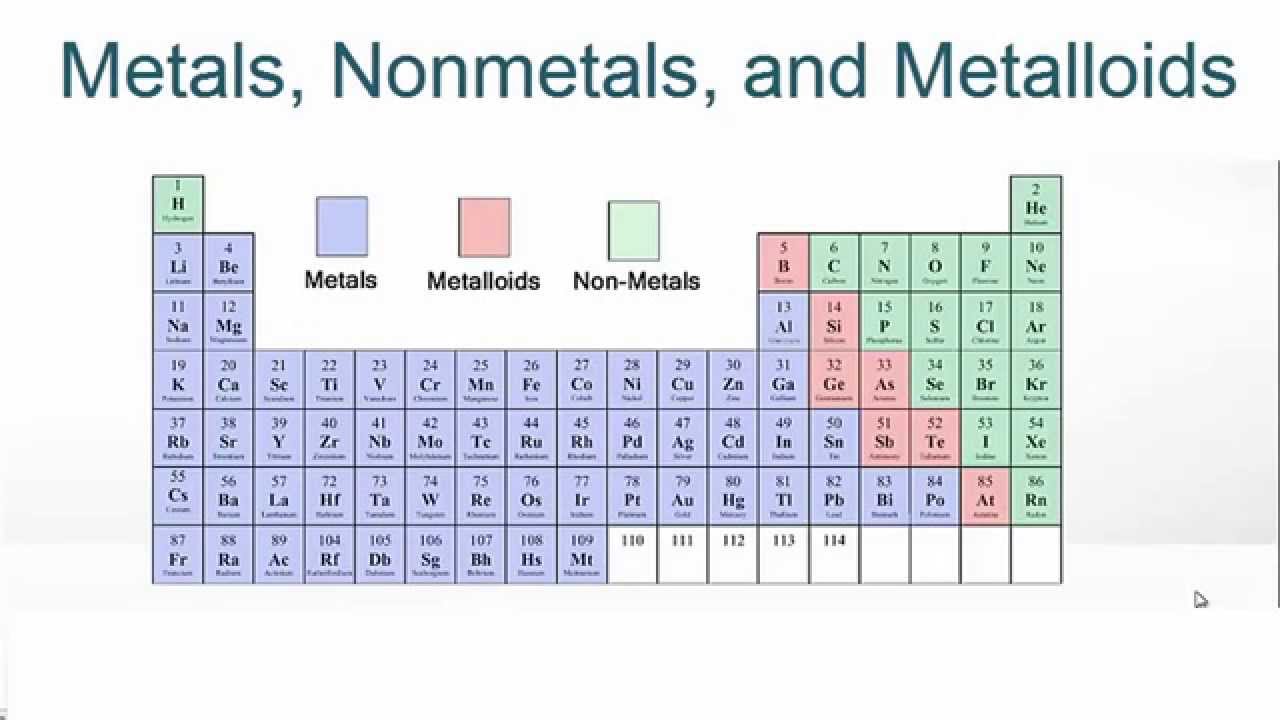
The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.

Metals nonmetals and metalloids on periodic table. Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table. Key Differences Between Metals Non-Metals and Metalloids Metals are the elements which exhibit the highest degree of metallic behavior is known as metals on the contrary. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids on the Periodic Table - YouTube A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the.
These elements are called metalloids. Their shape can be easily changed into thin wires or sheets without breaking. The three types of elements occupy their own places in the Periodic Table.
The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image. The noble gases are almost completely inert.
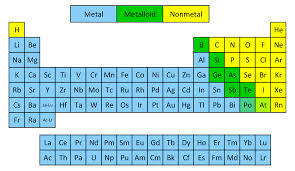
The metals green in the table nonmetals orange and metalloids blue. Metals are placed on the left side of the periodic table Non-metals are placed on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals.
Position in the Periodic Table. Most elements are metals. The metals are to the left of the line except for hydrogen which is a nonmetal the nonmetals are to the right of the line and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids.
1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND electricity a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 5 This tells you. SOLIDS LIQUIDS or GASSES What makes up most of the periodic table What is the classification of these characteristics. Metals Nonmetals Metalloids - Maze chase.
On many periodic tables a jagged black line see figure below along the right side of the table separates the metals from the nonmetals. The seven metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and polonium. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Chemistry 101 Periodic Table properties.
Metalloids tend to be economically important because of their unique conductivity properties they only partially conduct electricity which make them valuable in the semiconductor and computer chip industry. Metalloids are elements having a low degree of metallic behavior. They are usually shiny very dense and only melt at high temperatures.
Where at the metalloids located on the Periodic Table. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. The periodic table on the left separates elements into three groups.
The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids. Metals are elements having the highest degree of metallic behavior. The metalloids have some of the characteristics of metals and some of the characteristics of nonmetals.
Can a metalloid have properties of metals and nonmetals. An Introduction to General Organic and Biological Chemistry 12th. The metals are found on the left and the nonmetals are found on the right.
Metals are located in s p d and f blocks non-metals are located in s and p blocks whereas metalloids are located in p blocks of the periodic table Metals have high thermal and electrical conductivity while non-metals tend to be low and metalloids are good conductors. The Metalloids On the border between the metals and the nonmetals are seven elements called metalloids. Nonmetals are elements showing less or no metallic properties.
They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. Metals are at the left nonmetals are at the right and metalloids straddle a zig-zag line that separates metals from nonmetals. The most common metalloid is silicon Si.
Development of the Periodic table Effective Nuclear Charge Atomic and Ionic sizes. Learn about the metals nonmetals and metalloids and the periodic table. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
Where are metals located on the periodic table Most metals are. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals. Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Definition.
What is Carbon. Properties of Metalloids Metalloids are malleable and ductile Families Families in the periodic table share chemical properties because all elements in a family have the same number of valence electrons This means that all elements in a. The metalloids or semimetals have properties that are somewhat of a cross between metals and nonmetals.
Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals.
Taking physical properties into consideration they are more like the nonmetals but under certain circumstances contrary to the expected behaviour many of them can be made to conduct electricity. Metals non-metals and metalloids Moving from left to right across a period the elements become less metallic.
 The Parts Of The Periodic Table
The Parts Of The Periodic Table
Position in the Periodic Table.

List of metals nonmetals and metalloids. Herman Hoffmann and Ashcroft on the basis of relativistic modelling predict astatine will be a monatomic metal. List three differences in the physical properties between metals and nonmetals. The nonmetals lis t which makes up the periodic table includes hydrogen helium carbon sulfur nitrogen oxygen radon neon other halogens and noble gases etc.
The status of polonium and astatine is not settled. Metalloids have properties of both metals and nometals. This is related to the increase in the number of electrons in the outer shell of.
METALS NONMETALS METALLOIDS Classifying elements on the Periodic Table. 3 DIFFERENT TYPES OF ELEMENTS. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Definition. Their capacity to conduct electricity and heat is intermediate to that of metals and nonmetals. A Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 13 These elements do not have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 14 These elements are brittle and not ductile a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids d Nonmetals Metals e Nonmetals Metalloids f Metals Metalloids 15 These elements make up the majority of the periodic table and are found on the left side and middle of the periodic.
Determine whether the element Calcium is a metal or a. Share your videos with friends family and the world. 12 12 2013 12 07 59 pm.
The ability to conduct electrical or thermal energy. They are lustrous and are very brittle. List three differences in the physical properties between metals and nonmetals.
Check for Understanding Type your answer here Type your answer here. Nonmetals are elements showing less or no metallic properties. Metals non metals metalloids please list at least 4 physical properties of metals non metals and metalloids.
Pure 9997 iron chips electrolytically refined accompanied by a high purity 999999 6N 1 cm 3 cube. Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals. Elements categorized into metals non-metals and metalloids.
The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table. Silicon b fluorine c uranium d mercury e arsenic f iridium.
One useful way is by metals nonmetals and metalloids. Using the periodic table you can classify the elements in many ways. Na mg at rn.
Describe where Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids are on the periodic table. The periodic table is organized in families and periods. The word luster refers to which property of matter.
Compare Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids using their physical properties. Metals are elements having the highest degree of metallic behavior. Metals nonmetals and metalloids worksheet pdf.
Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. Most authors recognise one or the other or both as metalloids. Metals and nonmetals author.
Metalloids are elements having a low degree of metallic behavior. When elements combine to form compounds there are two major types of bonding that can result. The metals are to the left of the line except for hydrogen which is a nonmetal the nonmetals are to the right of the line and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids.
The metals list which makes up the periodic table includes iron lead gold aluminum platinum uranium zinc lithium sodium tin silver etc. The metalloids are intermediate in their properties between metals and nonmetals. Name period metals and nonmetals worksheet 1.
Identify the following as metals nonmetals or metalloids using the periodic table. The elements commonly classified as metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony and tellurium. Metals In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to.
Report an issue.