For comparison human red blood cells visible via light microscopy are approximately 8 µm wide or approximately 1000 times wider than a plasma membrane. The fluid mosaic model is one way of understanding biological membranes consistent with most experimental observations.
 Fluid Mosaic Model Advanced Definition Examples Diagrams
Fluid Mosaic Model Advanced Definition Examples Diagrams
Plasma membranes range from 5 -10 nm in thickness.
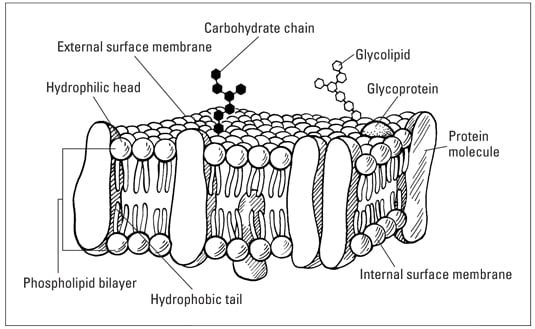
Example of fluid mosaic model. 2014 Vanessa Jason Biology Roots the cell membrane- Fluid Mosaic Model Student Directions- The oval at le is the cell membrane. The model that is now known to be correct for the structure of the biological membrane is. The fluid mosaic model depicts the structure of the plasma membrane as a variety of components which include phospholipids proteins and carbohydrates.
The cell membrane gets it fluidness because the phospholipids in a typical cell membrane are non bonded to one another. According to this model the cell membrane represents a fluid structure comprised of proteins within a phospholipid bilayer. The Fluid Mosaic Model of Biomembranes The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydratesthat gives the membrane a fluid character.
Nicolson in 1972 describes the cell membrane as a two-dimensional liquid that restricts the la. Their hydrophilic heads that dissolve easily in water meet the water medium in and out of the cell while their hydrophobic tails that do not dissolve are present inside the membrane. This model explains the structure of the plasma membrane of animal cells as a mosaic of components such as phospholipids proteins cholesterol and carbohydrates.
The fluid mosaic model is NOT related to the plasma membrane. A plasma membrane is a MOSAIC of components that move FREELY and FLUIDLY. Small amounts of carbohydrates are also found in the cell membrane.
There are restrictions to lateral movements and subdomains within the membrane have specific functions. The fluid mosaic model explains various observations regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydratesthat gives the membrane a fluid character.
These components give a fluid character to the membranes. The membrane is referred to as mosaic because like a mosaic that is made up of many different parts the cell membrane has a assorted composing of lipoids and proteins. The Fluid Mosaic Model of Membranes Membranes are vital structures found in all cells The cell surface membrane creates an enclosed space separating the internal cell environment from the external environment and intracellular membranes form compartments within the cell such as the nucleus mitochondria and RER.
First lets discuss the most abundant lipids which include both phospholipids and cholesterol alongside. The mosaic model of membrane structure describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids proteins carbohydrates cholesterol and proteins that gives the membrane a fluid character. The plasma membrane is a MOSAIC.
Cut out the oval and paste it into your notebook. The FluidMosaic Membrane model. Example sentences from the Web for fluid mosaic model Some gay apps like the newer Mister have not subscribed to the communitytribe model.
Plasma membranes range from 5 to 10 nm in thickness. Singer and Garth L. The cell membrane is described to be fluid because of its hydrophobic components that are integrated into the membrane structure such as lipids and membrane proteins that move sideways throughout the membrane.
That means the membrane more like a fluid. In every plasma membrane lies a structural framework of different components with significant cellular functions making up a mosaic known as the fluid mosaic model. The biological model which was devised by SJ Singer and G.
The proportions of proteins lipids and carbohydrates in the plasma membrane are different from cell types. Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head pointing outside and a hydrophobic tail forming the inside of the bilayer. A short video on the Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane.
Experiments conducted in the late 1960s led to a new concept of membrane structure as detailed in the fluid mosaic model proposed in 1972. These integral molecules are separate yet loosely bound defining the cells border and providing fluidity for optimal function. The fluid mosaic model was proposed by SJ.
The Fluid Mosaic Model of Membranes Membranes are vital structures found in all cells The cell surface membrane creates an enclosed space separating the internal cell environment from the external environment and intracellular membranes form compartments within the cell such as the nucleus mitochondria and RER. Because the phospholipids that form the cell membrane are a fluid substance the membrane is also considered a fluid structure similar to oil floating on the surface of water. We are building a mosaic of colored 8les to depict the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane.
The plasma membrane creates a specialized FLUID that looks like a MOSAIC. According to this biological model there is a lipid bilayer in which protein molecules are embedded. The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure is a cell membrane that behaves like a two- dimensional liquid of mixed composition.
The lipid bilayer gives fluidity and elasticity to the membrane. Here are some examples. When the FluidMosaic Membrane Model F-MMM of biological membrane structure was first introduced in 1972 it was envisioned as a basic framework model for cell membranes that could explain existing data on membrane proteins and lipid structures and their dynamics and help plan and predict future experimental outcomes.
The heterogeneous nature of natural membranes is described by the fluid mosaic model where the proteins are randomly dispersed in a two-dimensional lipid bilayer matrix. Consis8ng of the phospholipid bilayer proteins and filaments. This model states that the components of a membrane such as proteins or glycolipids form a mobile mosaic in the fluid-like environment created by a sea of phospholipids.
A short video on the Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane. The fluid mosaic model states that a cell membrane does not allow anything to pass through. The Fluid Mosaic Model states that membranes are composed of two layers of phospholipids molecules.
The Fluid part represents how some parts of the membrane can move around freely if they are not attached to other parts of the cell. Their hydrophilic heads that dissolve easily in water meet the water medium in and out of the cell while their hydrophobic tails that do not dissolve are present inside the membrane.
 The Fluid Mosaic Model A Level Notes
The Fluid Mosaic Model A Level Notes
The plasma membrane that surrounds these cells has two layers a bilayer of phospholipids fats with phosphorous attached which at body temperature are like vegetable oil fluid.
Fluid mosaic model definition. The Fluid Mosaic Model states that membranes are composed of a Phospholipid Bilayer with various protein molecules floating around within it. A phospholipid bilayer with protein molecules inserted patchwork-style throughout. The cell membrane is the thin layer that encloses a cells cytoplasm which is the substance between its membrane and its nucleus.
According to this model the plasma membrane is similar to a fluid in which various molecules are arranged in a mosaic-like pattern. The biological model which was devised by SJ Singer and G. Nicolson in 1972 to describe the structure of cell membranes Singer and Nicolson 1972.
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of componentsincluding phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydratesin which the components are able to flow and change position while maintaining the basic integrity of the membrane. According to this biological model there is a lipid bilayer in which protein molecules are embedded. Biological cell membranes are fluid membranes as depicted by the fluid mosaic model of phospholipids and proteins.
The fluid mosaic model explains various observations regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. Collins Dictionary of Medicine Robert M. Small amounts of carbohydrates are also found in the cell membrane.
The fluid-mosaic model describes the plasma membrane of animal cells. The fluid mosaic model is one way of understanding biological membranes consistent with most experimental observations. Plasma membranes range from 5 to 10 nm in thickness.
The Fluid Mosaic Model represents the complete cell membrane structure. This model states that the components of a membrane such as proteins or glycolipids form a mobile mosaic in the fluid-like environment created by a sea of phospholipids. The fluid mosaic model was first proposed by S.
The Fluid Mosaic Model states that membranes are composed of two layers of phospholipids molecules. The model likens the membrane to a mosaic of different components consisting of a fluid or elastic double layer made up of lipid molecules and large protein molecules. It describes the structure of cell membranes where a flexible lipid layer is spread with large protein molecules that act as channels through which other molecules enter and exit any cell.
The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. The fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane is the most accepted hypothesis which describes the membranous components and their functions. Because the phospholipids that form the cell membrane are a fluid substance the membrane is also considered a fluid structure similar to oil floating on the surface of water.
There are restrictions to lateral movements and subdomains within the membrane have specific functions. The lipid bilayer gives fluidity and elasticity to the membrane. The protoplasm of every living cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane.
Cell membrane health your door to health Branton 1966. Nicolson in 1972 describes the cell membrane as a two-dimensional liquid that restricts the la. In this now-accepted theory about cell structure phospholipid molecules each with one hydrophobic and one hydrophilic end make up most of the membrane.
The model that is now known to be correct for the structure of the biological membrane is. Fluid mosaic model definition. Plasma membranes range from 5 to 10 nm in thickness.
Some of these proteins are intrinsic they are completely embedded in the bilayer and others are extrinsic they are only partially embedded. The phospholipid layer has the physical properties of a fluid so that the proteins can move about relatively freely. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes SJ.
The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like because it is made up of a bunch of different molecules that are distributed across the membrane. Fluid mosaic model A widely accepted account of the structure of the cell membrane as consisting of a two-molecule layer of phospholipid with proteins embedded in it. The fluid mosaic model is a way of describing the structure of cell membranes.
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydratesthat gives the membrane a fluid character. The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydratesthat gives the membrane a fluid character. The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components including phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydratesthat gives the membrane a fluid character.