The number of the energy level is equal to the number of sub levels it has. The order of the electron orbital energy levels starting from least to greatest is as follows.
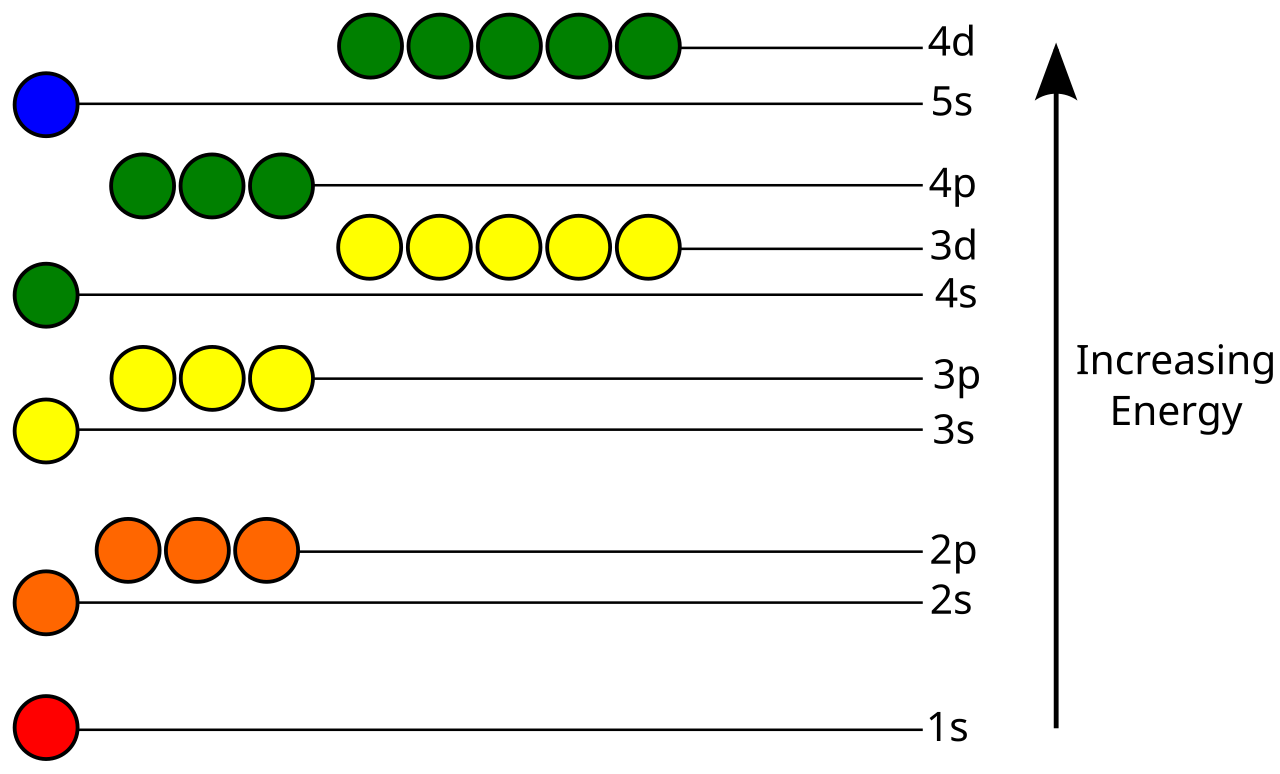 File Atomic Orbital Energy Levels Svg Wikimedia Commons
File Atomic Orbital Energy Levels Svg Wikimedia Commons
In the n1 shell you only find s orbitals in the n2 shell you have s and p orbitals in the n3 shell you have s p and d orbitals and in the n4 up shells you find all four types of orbitals.
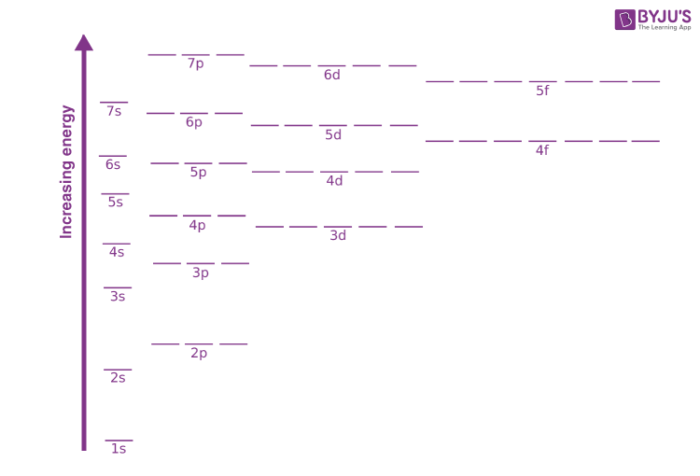
Energy levels and orbitals. Thus the energy value of an electron having a particular quantum is fixed irrespective of the orbital to which it may belong. Orbitals are named as s p d and f. These are spherical Every energy level contains one S-Orbital An S-Orbital in the first energy level is a 1s orbital An S-Orbital in the second energy level is a 2s orbital etc.
At the higher levels the lobes get more elongated with the most likely place to find the electron more distant from the nucleus. The orbits are analogous to a set of stairs in which the gravitational potential energy is different for each step and in which a ball can be found on any step but never in between. Each energy level consists of a number of sub levels which are labelled as spd or f.
It determines the shape of the orbitals and the energy of each level within a given principal quantum number. At the third level there is a set of five d orbitals with complicated shapes and names as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals 3px 3py 3pz. Lifting of degeneracy by an external magnetic field In case of the strong-field Zeeman effect when the applied field is strong enough so that the orbital and spin angular momenta decouple the good quantum numbers are now n l m l and m s.
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p. Calculating the Energy Level of an Orbital Since the electrons are negatively charged particles they repel each other. There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels - 3p x 3p y 3p z 4p x 4p y 4p z and so on.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow. All levels except for the first level have p orbitals. As with many processes in the quantum world this process is impossible to visualize.
The laws of quantum mechanics describe the process by which electrons can move from one allowed orbit or energy level to another. For example a 3s orbital is lower in energy than a 3p orbital which is lower in energy than a 3d orbital. A σ ns bonding molecular orbital and a σ ns antibonding molecular orbital.
At the third level there are a total of nine orbitals altogether. The stability of an atom depends on the. An orbital is the most probable region where an electron can be found around the nucleus.
The closer the. In addition to s and p orbitals there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. Orbitals - Orbital Energy Orbital energy level The energy of an electron in a single atom can be determined solely by the principal quantum number.
Is called the Bohr MagnetonThus depending on the value of each degenerate energy level splits into several levels. Orbitals can be ranked in the increasing order of orbital energy as follows. The lowest energy level electron orbitals are filled first and if there are more electrons after the lowest energy level is filled they move to the next orbital.
As we go down the periodic table the atomic number increases and another factor comes in to play here ie shielding. The other identifying feature of an orbitals for their representation as s p d and f is the angular momentum quantum number l. In most cases only the electrons contained in the s and p orbitals are considered valence electrons Electrons seek the lowest energy level possible.
There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s p d and f sharp principle diffuse and fundamental. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d. Orbitals and Energy Levels Electrons are arranged in energy levels around the nucleus of an atom.
In other words the energy associated with electrons in s p d and f orbitals of a particular principal quantum number is the same. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbitals and quantum numbers. Because each alkali metal M has an ns1 valence electron configuration the M 2 molecule has two valence electrons that fill the σ ns bonding orbital.
Energy levels are named as K L M N. It discusses the difference between atomic energy levels and. These spaces called orbitals are of different shapes denoted by a letter s p d f g.
σ 1s. The p orbitals at the second energy level are called 2p x 2p y and 2p z. Within each energy level is a volume of space where specific electrons are likely to be located.
For example the energy level of 3s 3p and 3d orbitals is equal. Within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. Difference Between Orbitals and Energy Levels Definition.
Only two energy levels are important for describing the valence electron molecular orbitals of these species.