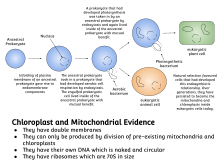
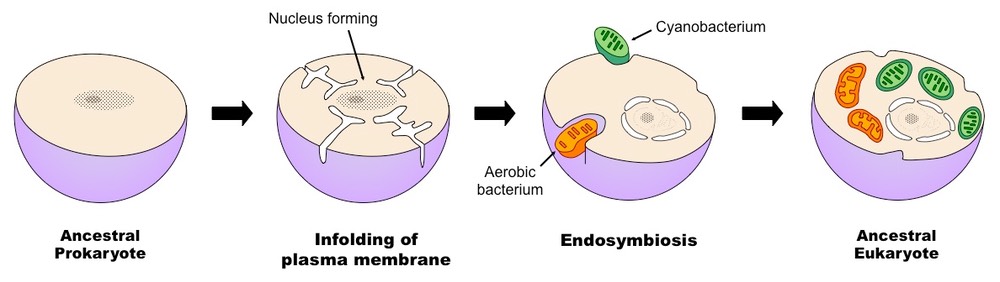
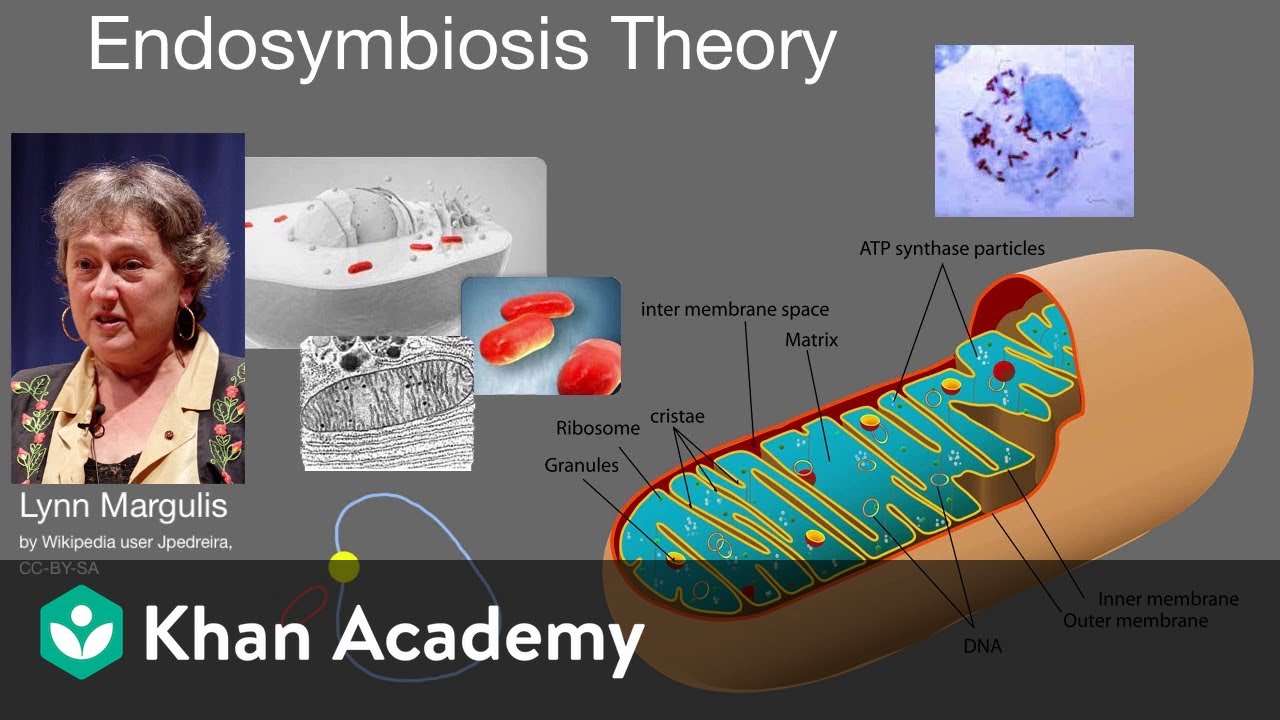
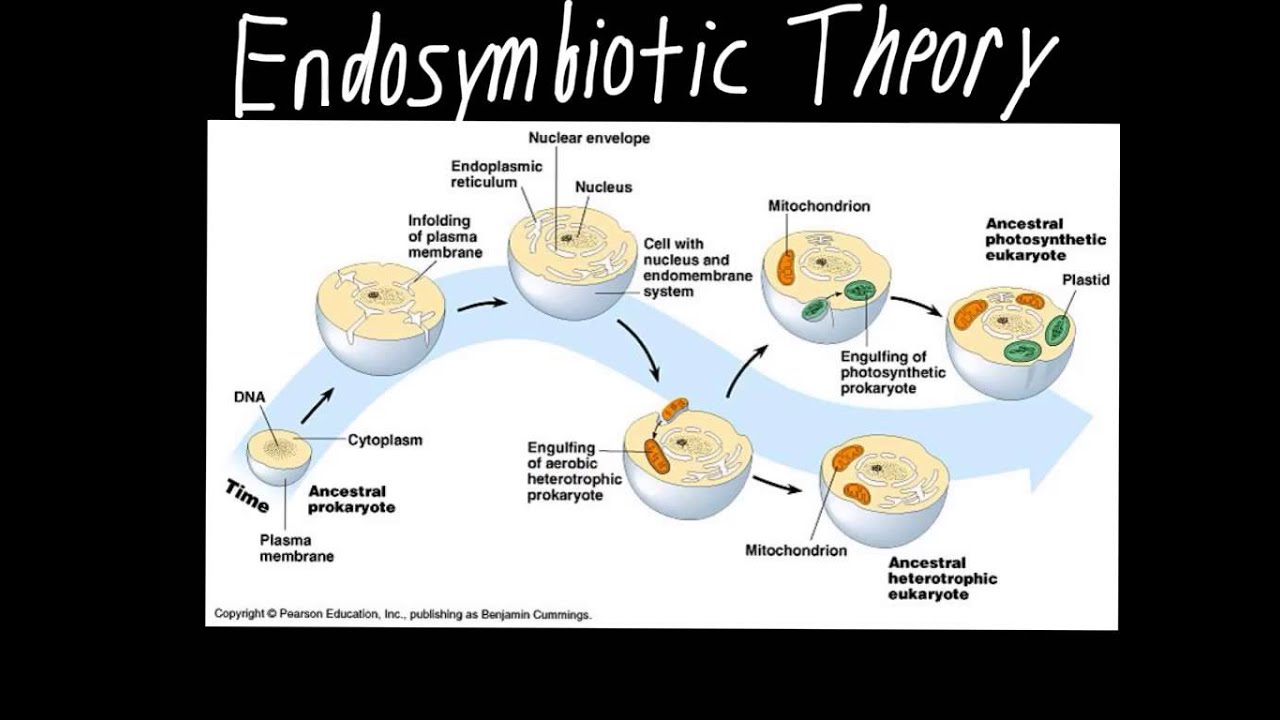
The structures and functions of the first were ultimately incorporated Read More. The endosymbiotic theory is the accepted mechanism for how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.
Fhs Bio Wiki Endosymbiotic Theory
The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in todays eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
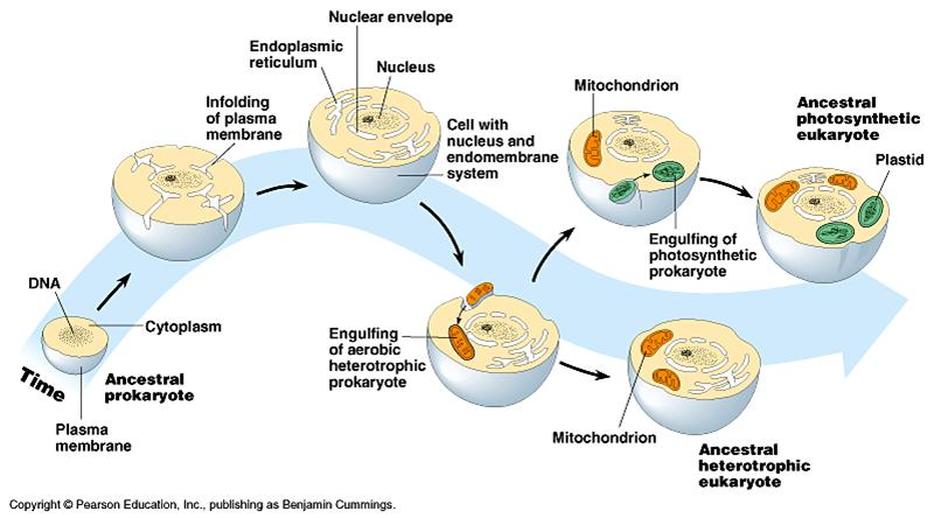
What is endosymbiosis theory. Thats when one organism or more lives inside another the two being mutually dependent upon each other. The Modern Synthesis established that over time natural selection acting on mutations could generate new adaptations and new species. A Theory in Crisis BY JEFFREY P.
P143 The theory was first suggested by the Russian botanist Mereshkovsky in 1905. Based on decades of accumulated evidence the scientific community supports Marguliss ideas. Endosymbiosis theory describes the mechanism by which mitochondria and chloroplasts entered eukaryotic cells.
Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells. However there are only shallow grounds for finding Darwinian concepts or population genetic theory incompatible with endosymbiosis. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms.
Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell. Endosymbiosis is a primary force in eukaryotic cell evolution. In this theory the first eukaryotic cell was probably an amoeba-like cell that got nutrients by phagocytosis and contained a nucleus that formed when a piece of the cytoplasmic membrane pinched off around the chromosomes.
Hence it is an accepted theory in biology. The endosymbiotic hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts suggests that mitochondria are descended from specialized bacteria probably purple nonsulfur bacteria that somehow survived endocytosis by another species of prokaryote or some other cell type and became incorporated into the cytoplasm. Endosymbiosis is important because it is a theory that explains the origin of chloroplast and mitochondria.
3 The heart of this explanation is the fact that the mitochondrion possesses a small circular piece of DNA containing some of the genes it. It involves a cooperative relationship between two cells which allow both to surviveand eventually led to the development of all life on Earth. The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion.
Symbiosis is a close relationship between two different organisms. The endosymbiosis theory explains how eukaryotic cells may have evolved from prokaryotic cells. Endosymbiotic theory holds that chloroplasts and mitochondria came about through the evolution of blue-green algae and bacteria through endocytosis.
Whats more the evidence for endosymbiosis applies not only to mitochondria but to other cellular organelles as well. According to SET certain primitive prokaryotes were engulfed by other different prokaryotes. In more recent times Lynn Margulis has argued vigorously along these lines.
Endosymbiotic theory Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was postulated by the American evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes more closely related to bacteria than archaea taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory.
Margulis and others hypothesized that chloroplasts bottom evolved from cyanobacteria top. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells. The serial endosymbiosis theory or SET offers one explanation of the origin of cytoplasmic organelles particularly the mitochondria and plastids found in many protists.
An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. Recent studies of algal evolution have shown that endosymbiosis has occurred several times and has yielded a variety of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures.
In eukaryotic cells the chloroplast and mitochondrion organelles are believed to stem from endosymbiosis see Endosymbiosis Theory first s. Endosymbiosis is a hypothesized process that explains the origin of the eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic cell. Endocytosis occurs when a substance passes into a cell through the cells membrane and then the cell plasma fuses together to keep the material inside forming an intracellular vesicle.
It is also a theory that explains how eukaryotic cells came to be. Been quite popular for about 50 years is that mitochondria and chloroplasts were derived from a mythical process called endosymbiosis. It is one of the most important events associated with evolution.
Historically conceptualizations of symbiosis and endosymbiosis have been pitted against Darwinian or neo-Darwinian evolutionary theory. Endosymbiont theory is the idea that eukaryote cells arose in evolution by the fusion of previously free-living protists prokaryotes.
 The Endosymbiotic Theory Biochemistry World
The Endosymbiotic Theory Biochemistry World
 Endosymbiosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Endosymbiosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
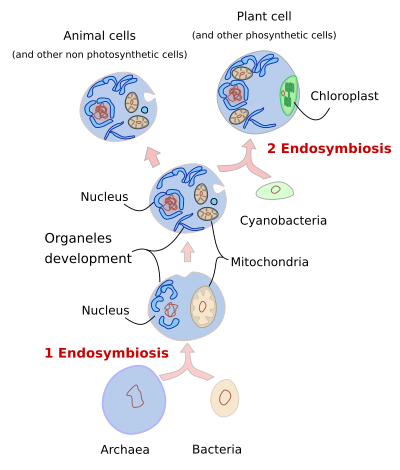 The Cell 1 Endosymbiosis Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
The Cell 1 Endosymbiosis Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
 Endosymbiotic Theory Risser Microbiology F2017 Openstax Cnx
Endosymbiotic Theory Risser Microbiology F2017 Openstax Cnx
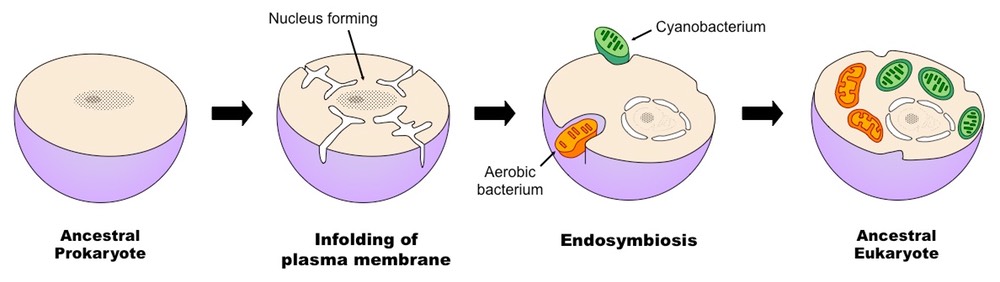 How Would You Define Endosymbiotic Theory Socratic
How Would You Define Endosymbiotic Theory Socratic
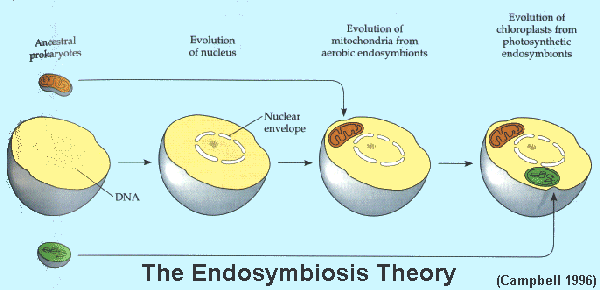 How Did Endosymbiosis Happen Socratic
How Did Endosymbiosis Happen Socratic
 Endosymbiotic Theory Definition And Evidence Biology Dictionary
Endosymbiotic Theory Definition And Evidence Biology Dictionary
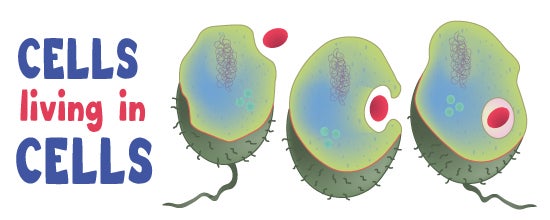 Endosymbiotic Theory Ask A Biologist
Endosymbiotic Theory Ask A Biologist
/2000px-Celltypes.svg-58f4417b3df78cd3fcb40917.png) Endosymbiotic Theory How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve
Endosymbiotic Theory How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve