A spring constant is a variable used in physics to describe the force per unit of distant a spring will resist or apply to an object. If the spring constant is zero it means that the stiffness of the spring will be zero.
 The Physics Of Springs How Manufacturers Understand Spring Design
The Physics Of Springs How Manufacturers Understand Spring Design
It is different for different springs and materials.

Spring constant in physics. The ratio of the change in length of spring A to the change in length of spring B is. X is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. A spiral spring a set of weights a weight hanger a balance a stop watch and a two- meter stick.
The variables of the equation are. There are different types of spring. If you think about what this means in terms of units or inspect the Hookes law formula you can see that the spring constant has units of force over distance so in SI units newtonsmeter.
Spring A has constant 100 Nm spring B has constant 200 Nm. This video covers- The types of elasticity compress stretch bending- The types of deformation elastic inelastic - Hookes Law- Idea of extension- S. Find the spring constant for spring if it requires a 9000 Newton force to pull spring 300 cm from the position of equilibrium.
K frac-Fx In this example a 9000 N force is pulling on a spring. So these are our properties to describe the. The spring constant is a mathematical parameter present in Hookes law the mathematical law that describes the stored potential energy of a coiled or stretched spring.
The spring constant shows how much force is needed to compress or extend a spring or a piece of elastic material by a given distance. Spring A has the original length of 60 cm and spring B has the original length of 90 cm. K is known as the spring constant or stiffness constant.
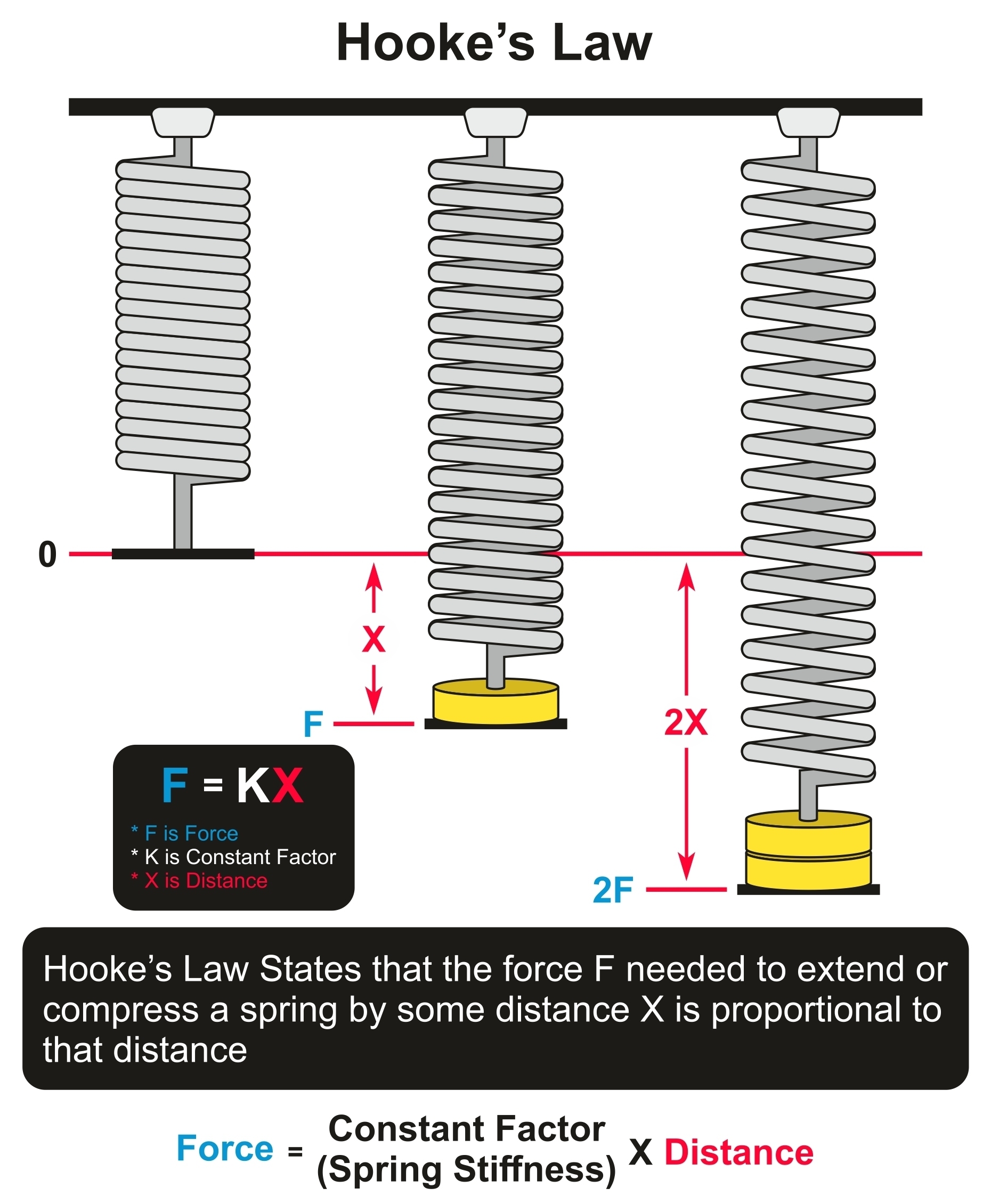
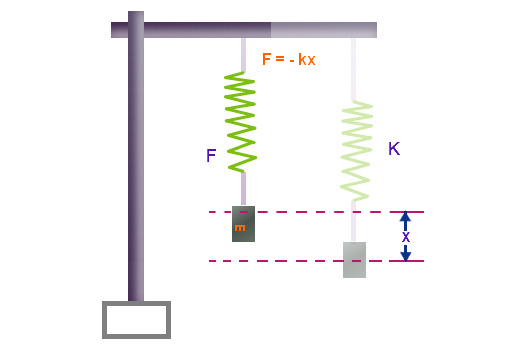
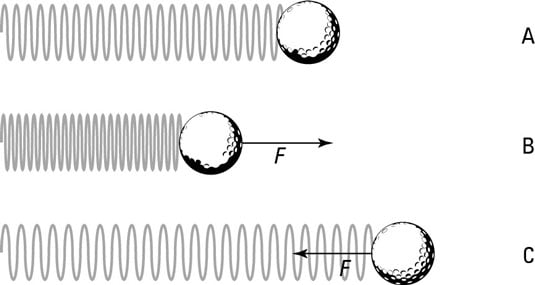
Hookes law is a law of physics that states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance x scales linearly with respect to that distancethat is F s kx where k is a constant factor characteristic of the spring ie its stiffness and x is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. Spring Constant 66 THE SPRING CONSTANT Objective. F -K x.
Where k is the spring constant. So in other words it is directly proportional to each other. According to Newtons third law if a spring is stretched or compressed using force F as a reaction the spring also react by a force - F.
It will no longer be a spring as no force will be acting in the opposite direction. Hookes Law and Spring Constant Hookes law which we sometimes refer to as the law of elasticity was discovered by an English scientist Robert Hooke in the year 1660. In other words the spring constant is the force applied if the displacement in the spring is unity.
For comparatively small distortions of an object the displacement or size of the distortions is directly proportional to the distortion force or load says the Hookes Law. F which represents force k which is called the spring constant and measures how stiff and strong the spring is and x is the distance the spring is stretched or compressed away from its equilibrium or rest position. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist.
To determine the spring constant of a spiral spring by Hookes law and by its period of oscillatory motion in response to a weight. Problems with Detailed Solutions Problem 1 What is the magnitude of the force required to stretch a 20 cm-long spring with a spring constant of 100 Nm to a length of 21 cm. For example torsion spring which works due to turning of the spring.
Equivalent Spring Constant Series When putting two springs in their equilibrium positions in series attached at the end to a block and then displacing it from that equilibrium each of the springs will experience corresponding displacements x 1 and x 2 for a total displacement of x 1 x 2We will be looking for an equation for the force on the block that looks like. The spring constant represents the stiffness of the spring. Hence it should always have a positive value.
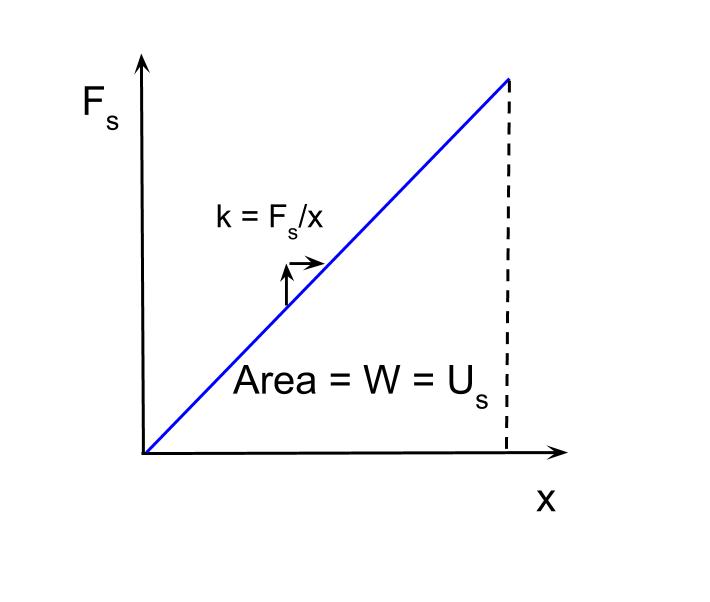
It is a measure of the elasticity of the spring. The larger the spring constant the stiffer the spring and the more. The spring constant k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring.
Unit of spring constant is Nm. If a force F is considered that stretches the spring so that it displaces the equilibrium position by x. The spring constant tells u that it is the ratio of change of force with respect of deflection.
Spring Constant Dimensional Formula. K is the spring constant in Nm-1. The spring constant can also be known as the force constant.
In other words its a measure of how stiff a spring is. The higher the constant the stiffer the spring. The spring constant is a number that represents how much force it takes to stretch a material -- materials with larger spring constants are stiffer.
Freely falling objects problems and solutions 3. To solve for the spring constant k we can rearrange the formula for spring constant as.
 Practice Applying Spring Constant Formulas Physics Class Video Study Com
Practice Applying Spring Constant Formulas Physics Class Video Study Com
 Laboratory Finding The Spring Constant
Laboratory Finding The Spring Constant
Hooke S Law Spm Physics Form 4 Form 5 Revision Notes
 Spring Constant Dimensional Formula With Solved Examples
Spring Constant Dimensional Formula With Solved Examples
Spring Constant Archives Regents Physics
 Spring Potential Energy And Hooke S Law Review Article Khan Academy
Spring Potential Energy And Hooke S Law Review Article Khan Academy
 Hooke S Law Calculate The Force From A Spring When Given Its Spring Constant And Deflection Calculate A Spring Constant Given The Required Force And Ppt Download
Hooke S Law Calculate The Force From A Spring When Given Its Spring Constant And Deflection Calculate A Spring Constant Given The Required Force And Ppt Download
 How To Calculate A Spring Constant Using Hooke S Law Dummies
How To Calculate A Spring Constant Using Hooke S Law Dummies
 Hooke S Law The Spring Constant Definition Equation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Hooke S Law The Spring Constant Definition Equation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
 Hooke S Law Physics Basic Introduction Restoring Force Spring Constant Practice Problems Youtube
Hooke S Law Physics Basic Introduction Restoring Force Spring Constant Practice Problems Youtube