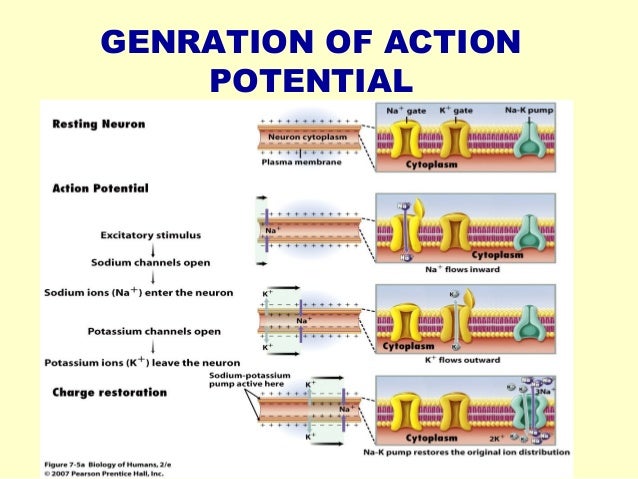
Nowadays nerve impulse and its conduction play a vital role in bio medical engineering. Nerve impulse is an overall physiological changes that occur in a neuron due mechanical chemical or electrical disturbance created by a stimulus.
 Neurons Structure And Conduction Of A Nerve Impulse Ppt Download
Neurons Structure And Conduction Of A Nerve Impulse Ppt Download
It is often done at the same time as an EMG in order to exclude or detect muscle disorders.
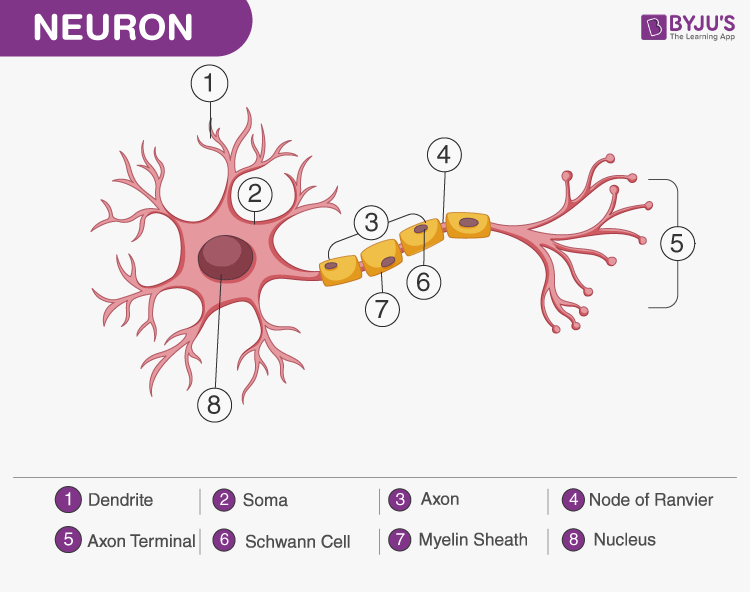
Conduction of nerve impulses. The SA node is located in the upper wall of the right atrium. Conduction of nerve impulse occurs due to the presence of active and electronic potentials along the conductors. Transmission of signals internally between the cells is achieved through a synapse.
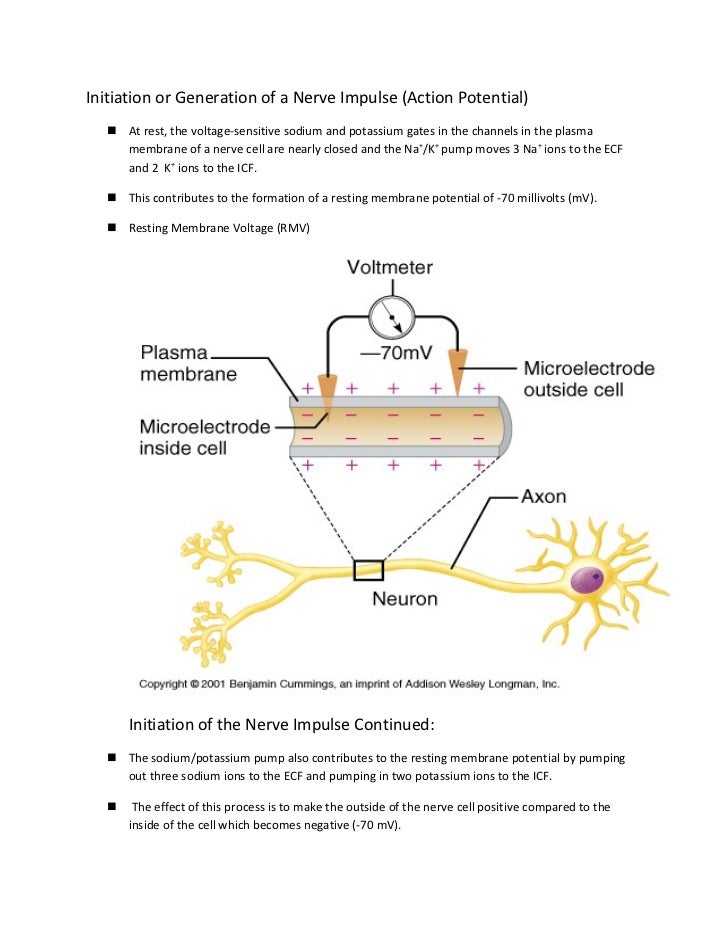
As an action potential nerve impulse travels down an axon there is a change in polarity across the membrane of the axon. Positive molecules are stored in membranes guarded by gated channels. The sinoatrial SA node also referred to as the pacemaker of the heart contracts generating nerve impulses that travel throughout the heart wall.
Hi friends here I am with another video. The electricity causes a change in polarity by opening channels to move positive sodium or potassium ions in or out. Myelinated axons conduct impulses about 10 times faster than comparable unmyelinated ones.
In conducting nerve impulse the following play a major role. The sheath insulates the axon and covers up the section beneath it. A nerve conduction velocity test measures how quickly electrical impulses move along a nerve.
Myelination significantly increases the speed impulses are conducted how does the axon diameter affect the speed of conductance. It is the. Nerve conductors comprise relatively higher membrane resistance and low axial resistance.
Myelination and Saltatory Conduction The presence of a myelin sheath increases the speed of conduction of nerve impulses. This video will help CONDUCTION OF NERVE IMPULSE I EASY WAY I NEET NCERTKeep supporting and sharing with friends. A lower proportion of ions leak in or out by diffusion How does the temperature affect speed of conduction.
Thicker fibers can maintain the resting potential more efficiently. Nerve cells neurons are specialized so that at one end there is a flared structure termed the dendrite. Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse Generation of nerve impulse is dependent on the strength of a stimulus which in turn triggers both chemical and electrical changes in neurons.
Axon- Helps in the propagation of nerve impulses to the target cell. In response to a signal from another neuron sodium- Na and potassium- K gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential. This causes both atria to contract.
It is a state of resting potential which is electrically charged but non-conductive. In nerve conduction both the electricity and the chemical molecules are together involved as electro chemical process. Electrical signals are carried by nerve cells to transfer signals from one nerve cell to another nerve cell.
It is the graded potential state where the threshold stimulus having a potential of -55 mV brings a. Transmission of Nerve Impulse Polarization. Notably the neural membrane harbours several ion channels which are selectively porous to different ions.
Nerve conduction velocity CV is an important aspect of nerve conduction studiesIt is the speed at which an electrochemical impulse propagates down a neural pathwayConduction velocities are affected by a wide array of factors including age sex and various medical conditions. The rapid conduction of impulses is essential in allowing the nervous system to mediate short-term and near immediate communication and control between various body systems. A nerve impulse begins conduction as electrical impulses initiated by the brain travel down through nervous system cells.
Axon Ending- Acts as a transmitter of signals. It propagation through axon synapse and neuromuscular junction is called Nerve Impulse conduction. Conduction of nerve impulses along nerve conductors occurs by means of electrotonic and action potentials which move along the fiber in both directions without transferring to neighboring fibers.
Nerve Impulse transmission along Neuron. Nerve Impulse Conduction Nerve impulse. The conduction of nerve impulse is one of the sub groups of biomedical engineering.
A healthy nerve conducts signals with greater speed and strength than a damaged nerve. Conduction of Nerve Impulse - This video defines nerve impulse and explains the mechanism involved in the transmission of nerve impulse. Dendrites- Receive the signals from the axon ends.
The first step of cardiac conduction is impulse generation. Pacemaker Impulse Generation. Transmission of intercellular signals is achieved through the synapses usually by means of mediators that induce postsynaptic potentials.
 Generation And Conduction Of Nerve Impulse Youtube
Generation And Conduction Of Nerve Impulse Youtube
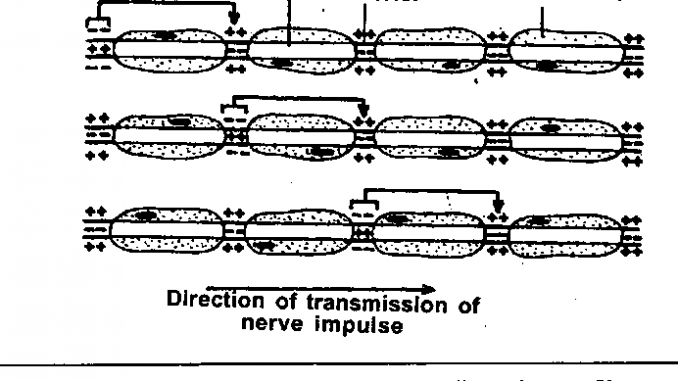 Nerve Impulse Conduction Online Biology Notes
Nerve Impulse Conduction Online Biology Notes
 Ppt Conduction Of Nerve Impulses Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4206308
Ppt Conduction Of Nerve Impulses Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4206308
 Nerve Impulse Definition Mechanism Process Types
Nerve Impulse Definition Mechanism Process Types
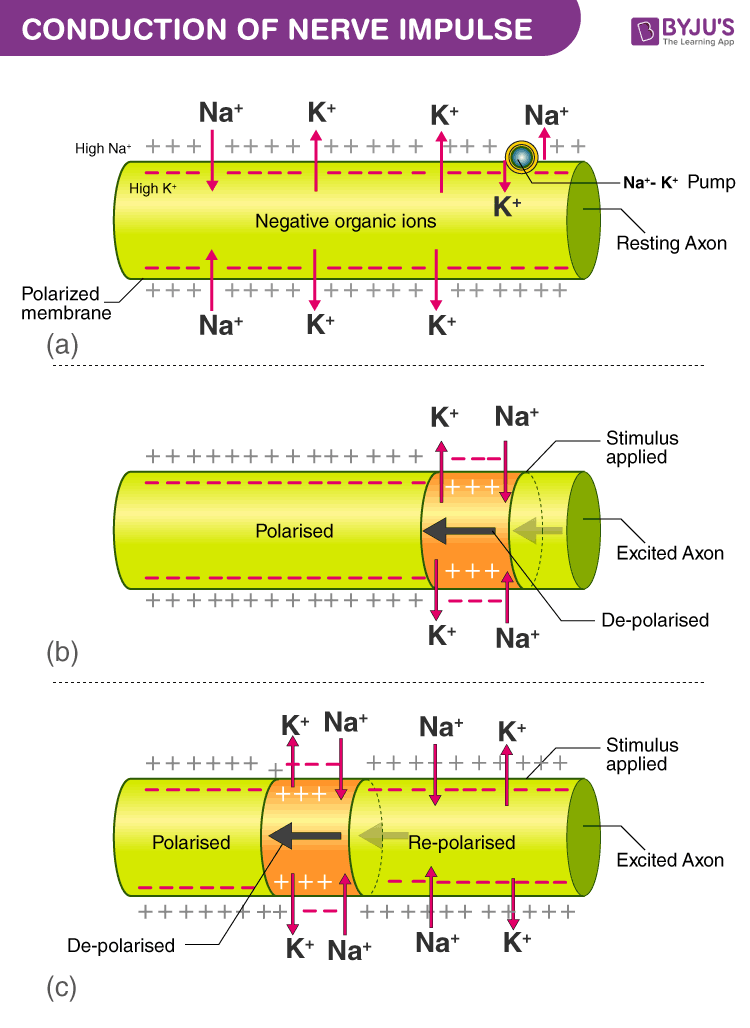 Nerve Impulse Conduction And Transmission Of Nerve Impulses
Nerve Impulse Conduction And Transmission Of Nerve Impulses

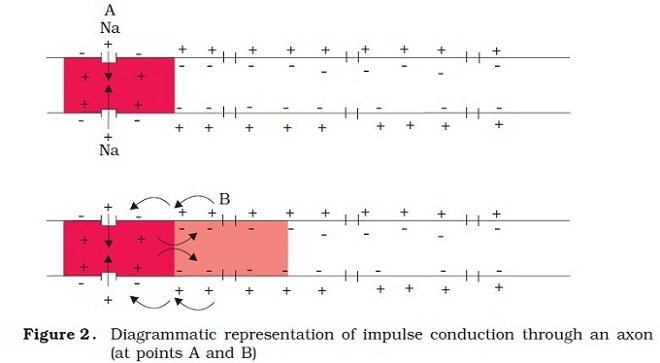 Generation And Conduction Of Nerve Impulse Definition Examples Diagrams
Generation And Conduction Of Nerve Impulse Definition Examples Diagrams
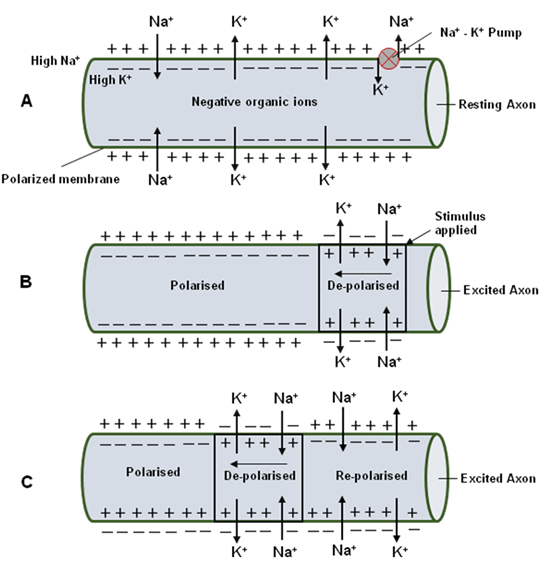 Nerve Impulse Conduction Online Biology Notes
Nerve Impulse Conduction Online Biology Notes
 Neurons Generation Conduction And Transmission Of Nerve Impulse
Neurons Generation Conduction And Transmission Of Nerve Impulse
Human Physiology Neurons The Nervous System
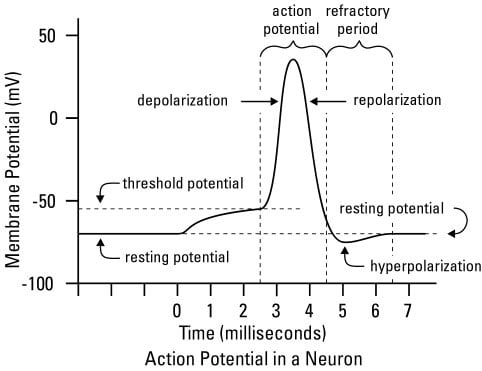 Understanding The Transmission Of Nerve Impulses Dummies
Understanding The Transmission Of Nerve Impulses Dummies